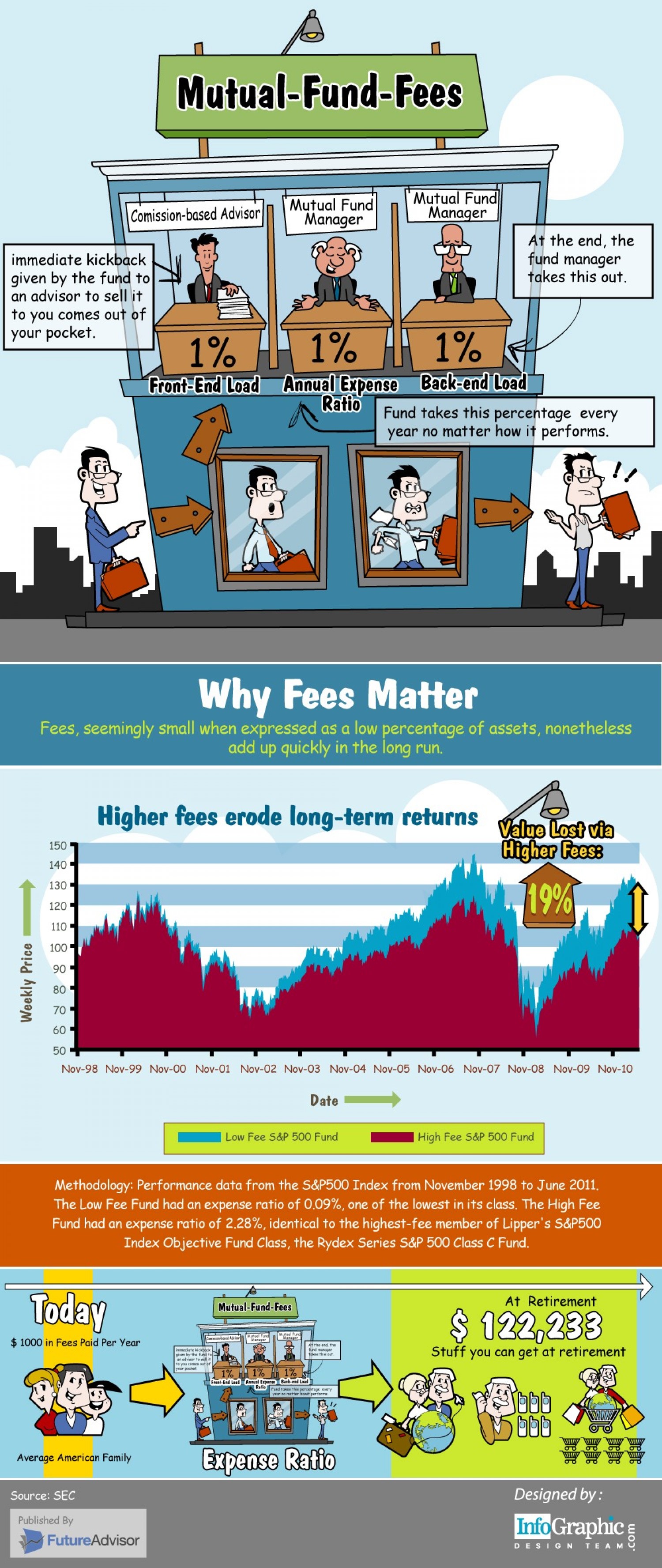
A Brief Overview of Annuities for Physicians
[By Gary A. Cook, MSFS, CFP®, CLU, ChFC, RHU, LUTCF, CMP™ (Hon)]
[By Kathy D. Belteau, CFP®, CLU, ChFC, FLMI]
[By Philip E. Taylor, CLU, ChFC, FLMI]
Introduction
Annuities were reportedly first used by Babylonian landowners to set aside income from a specific piece of farmland to reward soldiers or loyal assistants for the rest of their lives.
Today’s annuities substitute cash for farmland; however the concept is the same. In 1770, the first annuities were sold in the United States and were issued by church corporations for the benefit of ministers and their families. Annuities have grown on a tax-deferred basis since enactment of the Federal Income Tax Code in 1913. They began to gain widespread acceptance in the early 1980s when interest rates credited exceeded 10%. During the last two decades, annuities have been the fastest growing sector of premiums for life insurance companies.
Nevertheless, are they actually “needed” by contemporary physicians – – or merely “sold” to them?
An annuity is a legal contract between an insurance company and the owner of the contract. The insurance company makes specific guarantees in consideration of money being deposited with the company.
Annuities are generally classified as fixed or variable – deferred or immediate. As their names indicate, deferred annuities are designed as saving funds to accumulate for future use.They are growth-oriented products where the tax on the interest earned is deferred until the money is withdrawn. An immediate annuity is used for systematically withdrawing money without concern for the money lasting until the end. The insurance company assumes this risk.
Deferred Annuities
The deferred annuity contract, like a permanent life insurance policy, has been found by some to be a convenient method of accumulating wealth. Funds can be placed in deferred annuities in a lump sum, called Single Premium Deferred Annuities, or periodically over time, called Flexible Premium Deferred Annuities. Either way, the funds placed in a deferred annuity grow without current taxation (tax-deferred). .
Fixed Deferred Annuity
Fixed deferred annuities provide a guaranteed minimum return of return (usually around 3 percent per year) and typically credit a higher, competitive rate based on the current economic conditions.
Fixed annuities are usually considered conservative investments as the principal (premium) is guaranteed not to vary in value. Insurance companies are required by state insurance laws to maintain a reserve fund equal to the total value of fixed annuities. Fixed annuities are also protected by State Guaranty Fund Laws.
Example:
Dr. Park, a retired physician, desires a safe financial vehicle for $100,000 of her excess savings. She doesn’t need the earnings of this investment for current income and also wants to reduce her income tax liability. She decides to purchase a fixed deferred annuity with her $100,000. The annuity guarantees a 3 percent annual return and the current rate is 6 percent.
After the first year, $6,000 of interest is credited to the annuity and Dr. Park has no current income taxes as a result. If the 6 percent interest rate does not change, after 3 years, the annuity will have $119,102 of value.
Variable Deferred Annuity
Recently, variable deferred annuities have become very popular. Like fixed annuities, variable deferred annuities offer tax-deferred growth, but this is where the similarities end. Variable annuities are not guaranteed. The appreciation or depreciation in value is totally dependent on market conditions.
Variable deferred annuities assets are maintained in separate accounts (similar to mutual funds) that provide different investment opportunities. Most of the separate accounts have stock market exposure, and therefore, variable annuities do not offer a guaranteed rate of return.
But, the upside potential is typically much greater than that of a fixed annuity. The value of a variable deferred annuity will fluctuate with the values of the investments within the chosen separate accounts. Although similar to mutual funds, there are some key differences. These include:
· A variable annuity provides tax deferral whereas a regular mutual fund does not
· If a variable annuity loses money because of poor separate account performance, and the owner dies, most annuities guarantee at least a return of principal to the heirs. This guarantee of principal only applies if the annuity owner dies. If the annuity value decreases below the amount paid in, and the annuity is surrendered while the owner is alive, the actual cash value is all that is available.
· When money is eventually withdrawn from a deferred annuity, it is taxable at ordinary income tax rates. With taxable mutual funds, they can be liquidated and taxed at lower, capital gains rates.
· There is also a 10 percent penalty if the annuity owner is under 59½ when money is withdrawn. There is no such charge for withdrawals from a mutual fund.
· The fees charged inside of a variable annuity (called mortality and expense charges) are typically more than the fees charged by a regular mutual fund.
Assessment
Variable deferred annuities are sensible for physicians who want stock market exposure while minimizing taxes. Most financial advisors and Certified Medical Planners™ [CMP™] recommend regular mutual funds when the investment time horizon is under 10 years. But if the time horizon is more than 10 years, variable annuities may occasionally become more attractive because of the additional earnings from tax-deferral.
Both types of deferred annuities are subject to surrender charges. Surrender charges are applied if the annuity owner surrenders the policy during the surrender period, which typically run for 5 to 10 years from the purchase date. The charge usually decreases each year until it reaches zero. The purpose of the charge is to discourage early surrender of the annuity.
Equity Index Annuity
The equity index annuity combines the basic elements of both the variable and the fixed annuity. The credited interest earnings are generally linked to a percent of increase in an index, such as the Standard & Poor’s 500 Composite Stock Price Index (S&P 500). This percentage is called the Participation Rate and may be guaranteed for a specified period of up to 10 years or adjusted annually. Thus, the physician annuity owner is able to participate in a portion of market gains while limiting the risk of loss.
Typically, the indexed annuity has a fixed principal, with the insurance company and contract owner sharing the investment risk. If the S&P 500 Index goes up, so do interest earnings. If it declines, the insurance company guarantees the principal.
So, the physician contract owner accepts the risk of an unknown interest yield based on the growth or decline of the S&P 500. Medical professionals and healthcare practitioners should pay particular attention to surrender penalties, asset management fees and any monthly caps on appreciation.
Immediate Annuities
Immediate annuities provide a guaranteed income stream. An immediate annuity can be purchased with a single deposit of funds, possibly from savings or a pension distribution, or it can be the end result of the deferred annuity, commonly referred to as annuitization. Just like deferred annuities, immediate annuities can also be fixed or variable.
Immediate annuities can be set up to provide periodic payments to the policy owner annually, semiannually, quarterly or monthly. The annuity payments can be paid over life or for a finite number of years. They can also be paid over the life of a single individual or over two lives.

Immediate Fixed Annuity
Immediate fixed annuities typically pay a specified amount of money for as long as the annuitant lives.They may also be arranged to only pay for a specified period of time, i.e., 20 years. They often contain a guaranteed payout period, such that, if the annuitant lives less than the guaranteed number of years, the heirs will receive the remainder of the guaranteed payments.
A note of caution here, as the selection of an immediate annuity is an irrevocable decision!
Example:
Dr. Jones is 70 years old and retired. He is only of average wealth, but is concerned that if he lives too long, he could deplete his savings. He decides to use $100,000 and purchase a lifetime immediate annuity with 20 years certain. The insurance company promises to pay him $7,000 per year as long as he lives. If Dr. Jones dies four years after purchase, he would only have received $28,000 out of a $100,000 investment. However, his heirs will receive $7,000 for the next 16 years. If Dr. Jones survives to the age of 98, he would have received $196,000 (or 28 years of $7,000).
Immediate Variable Annuity
Immediate variable annuities provide income payments to the annuitant that fluctuates with the returns of the separate accounts chosen. The theory is that since the stock market has historically risen over time, the annuity payments will rise over time and keep pace with inflation. If this is indeed what happens, it is a good purchase, but it cannot be guaranteed.
Some companies will, at a minimum, provide a guarantee of a low minimum monthly payment no matter how poorly the separate accounts perform.
Split annuities
A popular method of adding income and yet still accumulating savings is through the use of two separate annuity policies. Part of the funds is placed in an immediate annuity to provide monthly income. The balance is placed in a deferred annuity grows to the total value of the premium paid for both annuities.
The income that is received from the Immediate Annuity includes a portion of the initial premium, as well as the taxable interest earned. Only the portion of income that is interest is taxable. The ratio between the annuity principal and interest being paid out is called an Exclusion Ratio.
Example:
Dr. Jeanne Jones has put $100,000 into a 5-year non-tax deferred vehicle at 5%. The earnings to supplement Jeanne’s retirement is $25,000. With a combined federal and state tax of 33%, the net after tax income would be $16,750. Jeanne takes the same $100,000 using the split annuity concept she would receive $24,444 over the 5 years. Based on an exclusion ration of 89%, her total taxable amount is $2,797. This would yield $923 in taxes at the same 33% tax rate. Jeanne would have $23,521 of spendable income with the split annuity compared to the $16,750.
Qualified Annuities
The term qualified refers to those annuities which permit tax-deductible contributions under one of the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) sections, i.e., § 408 Individual Retirement Accounts (IRA), § 403(b) Tax Sheltered Annuities, § 401(k) Voluntary Profit Savings Plans. Qualified annuities can also result from a rollover from such a plan.
Assessment
Currently, there is much lively debate in the industry as to whether an annuity, which is tax-deferred by nature, should be used as a funding vehicle within a tax-qualified plan, i.e., a tax-shelter within a tax-shelter. Since the investment options within the annuity are also generally available to the plan participant without the additional management expenses of the annuity policy, it is felt this could be a breach of fiduciary responsibility. And, most insurance agents are not fiduciaries.
Both the National Association of Securities Dealers (NASD) and the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) have gone on record as criticizing these sales.
However, there are numerous examples of deferred annuities that have outperformed similar investment-category mutual funds, even after taking the annuity expenses into account.
Conclusion
Your thoughts and comments on this ME-P are appreciated. Feel free to review our top-left column, and top-right sidebar materials, links, URLs and related websites, too. Then, subscribe to the ME-P. It is fast, free and secure.
Speaker: If you need a moderator or speaker for an upcoming event, Dr. David E. Marcinko; MBA – Publisher-in-Chief of the Medical Executive-Post – is available for seminar or speaking engagements. Contact: MarcinkoAdvisors@msn.com
OUR OTHER PRINT BOOKS AND RELATED INFORMATION SOURCES:
Filed under: CMP Program, Financial Planning, Glossary Terms, Insurance Matters, Investing, Recommended Books, Retirement and Benefits, Risk Management | Tagged: annuities, certified medical planner, CMP, deferred annuity, Financial Planning, FINRA, Flexible Premium Deferred Annuities., Insurance Matters, NASD, SEC, Single Premium Deferred Annuities, SIPC, variable annuity, wualified annuities, www.certifiedmedicalplanner.com | 6 Comments »