By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***
***
Commodities are essential raw materials that fuel the global economy, traded in markets and used in everything from food production to energy and manufacturing. Their value lies in their universality, stability, and role in investment strategies.
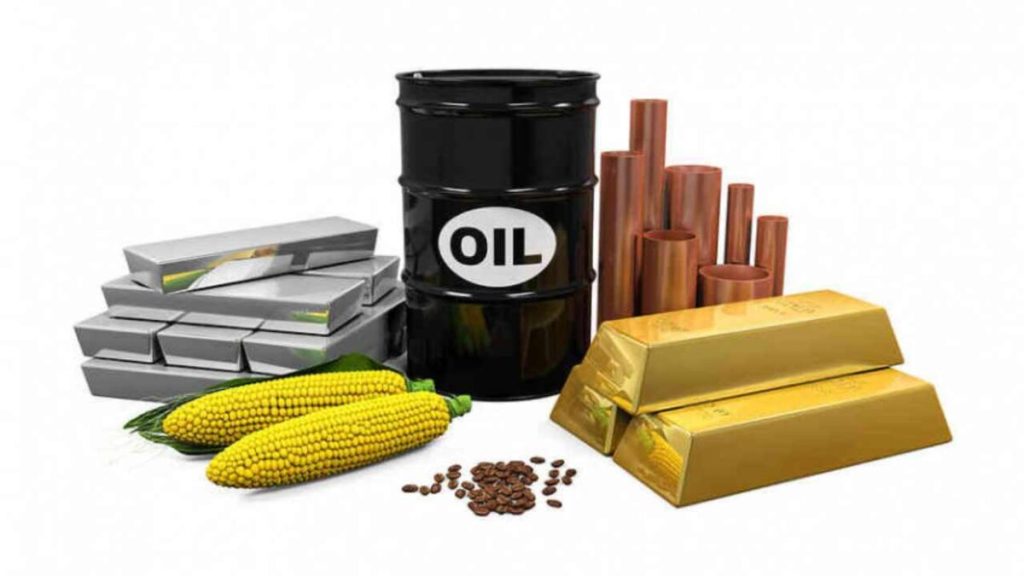
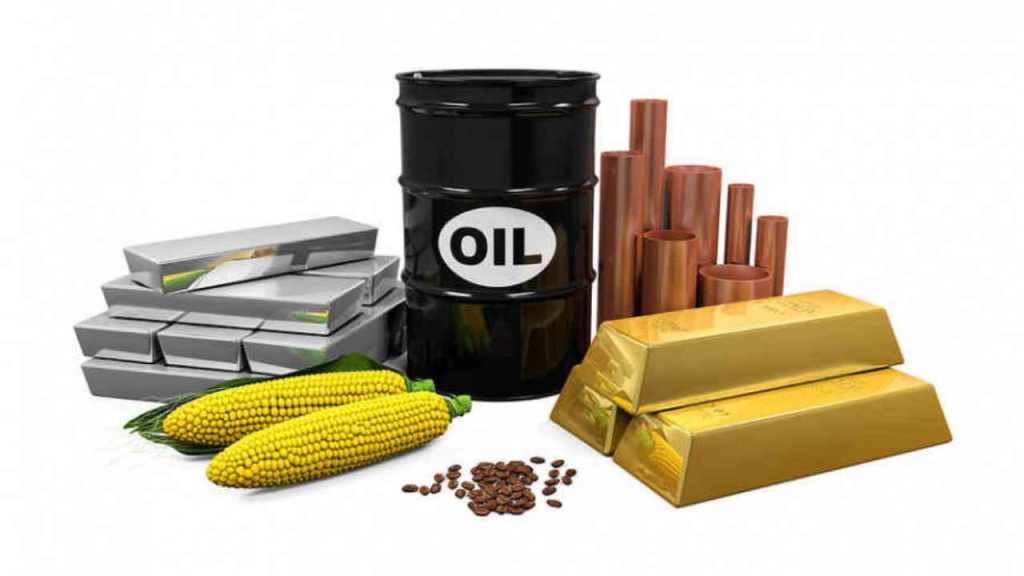
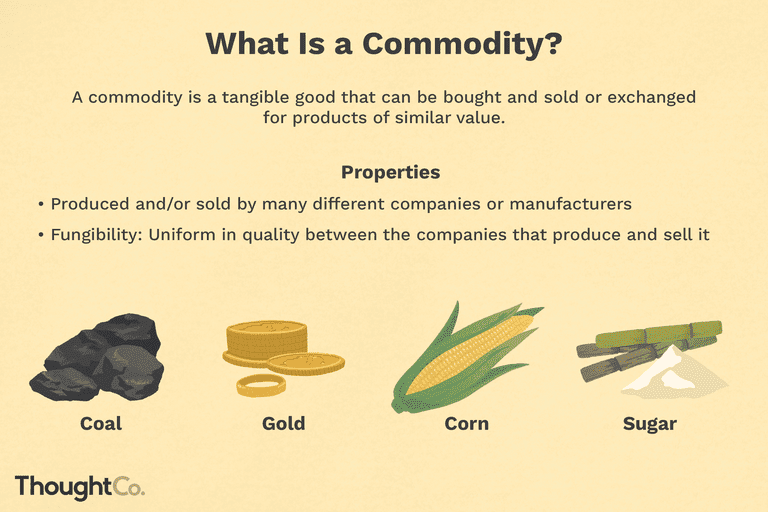
A commodity is a basic good used in commerce that is interchangeable with other goods of the same type. These raw materials are the building blocks of the global economy, ranging from agricultural products like wheat and coffee to natural resources such as crude oil, gold, and copper. Because commodities are standardized and widely used, they are traded on exchanges where their prices fluctuate based on supply and demand.
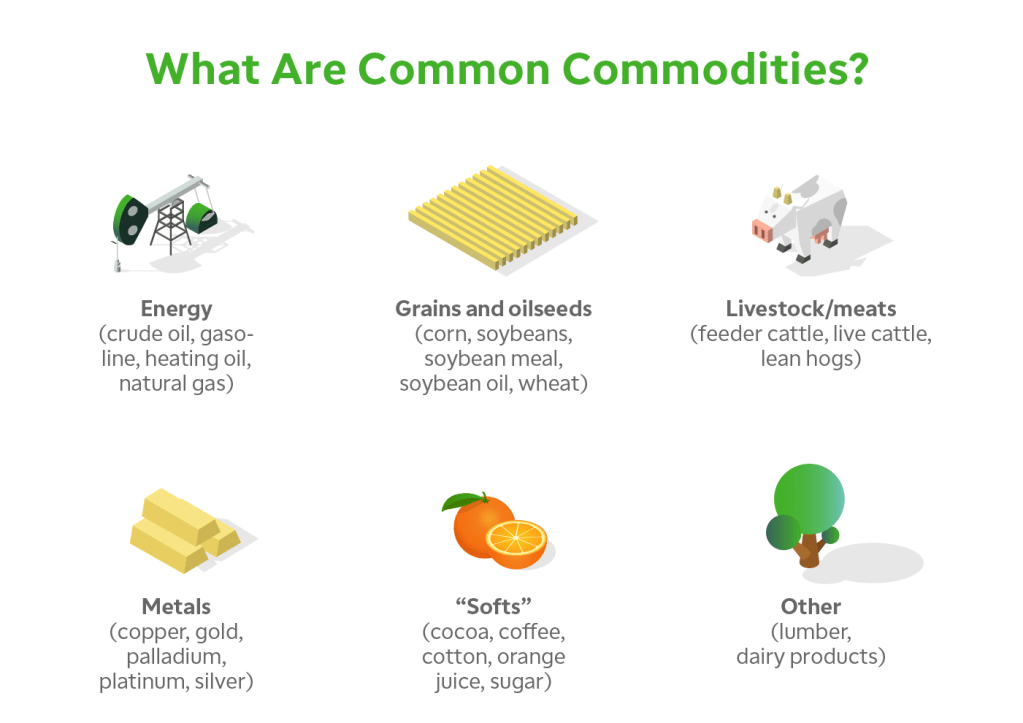
There are two main types of commodities: hard and soft. Hard commodities include natural resources that are mined or extracted—such as oil, gas, and metals. Soft commodities are agricultural products or livestock—like corn, soybeans, cotton, and cattle. These categories help investors and analysts understand market behavior and economic trends.
Commodities play a vital role in global trade. Countries rich in natural resources often rely on commodity exports to drive their economies. For example, oil-exporting nations like Saudi Arabia and Venezuela depend heavily on petroleum revenues. Similarly, agricultural powerhouses like Brazil and the United States benefit from exporting soybeans, coffee, and wheat. The prices of these commodities can significantly impact national income, inflation rates, and currency strength.
Commodity markets are also important for investors. Many people invest in commodities to diversify their portfolios and hedge against inflation. Since commodity prices often rise when inflation increases, they can act as a buffer against declining purchasing power. Investors can gain exposure to commodities through futures contracts, exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or direct ownership of physical goods. However, commodity investing carries risks, including price volatility due to weather events, geopolitical tensions, and changes in global demand.
One of the key features of commodities is their fungibility. This means that a unit of a commodity is essentially the same regardless of its origin. For example, a barrel of crude oil from Saudi Arabia is considered equivalent to one from Texas, as long as it meets the same grade. This standardization allows commodities to be traded efficiently on global markets.
Commodities also influence consumer prices. When the cost of raw materials rises, it often leads to higher prices for finished goods. For instance, an increase in wheat prices can make bread more expensive, while rising oil prices can lead to higher transportation and heating costs. This ripple effect makes commodity prices a key indicator of economic health.
In conclusion, commodities are foundational to both economic activity and investment strategy. They represent the raw inputs that power industries and sustain daily life. Understanding commodities—how they’re categorized, traded, and priced—offers insight into global markets and helps individuals and nations make informed financial decisions.
Whether you’re a consumer, investor, or policymaker, commodities are a crucial part of the economic landscape.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", finance, Glossary Terms, Portfolio Management, Touring with Marcinko | Tagged: coffee, commodities, copper, corn, cotton, david marcinko, economy, finance, gas, gold, Investing, oats, oil, silver, soybeans, wheat | Leave a comment »