By Staff Reporters
SPONSOR: http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
***
***
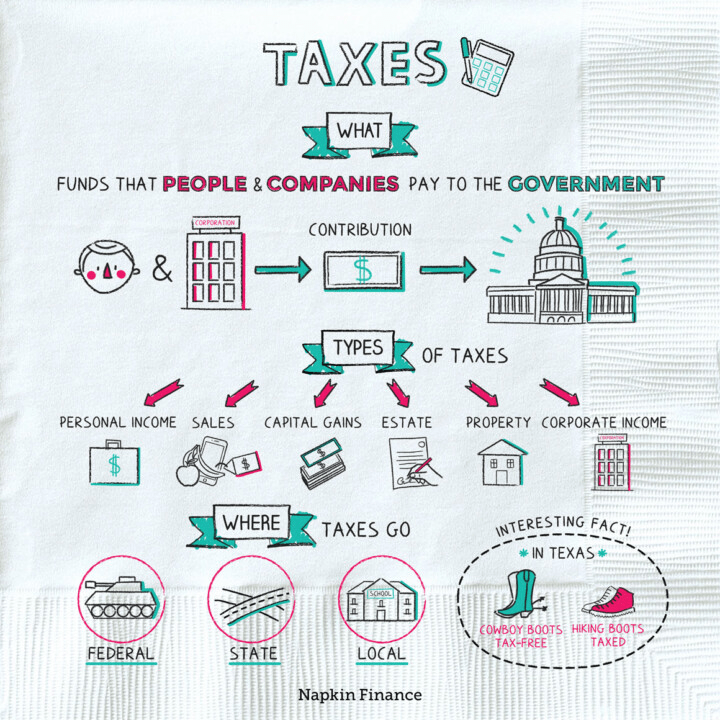
A concept of tax fairness that states that people with different amounts of wealth or different amounts of income should pay tax at different rates. Wealth includes assets such as houses, cars, stocks, bonds, and savings accounts. Income includes wages, interest and dividends, and other payments.
Gross income reduced by certain amounts, such as a deductible IRA contribution or student loan interest
Money that taxpayers must pay to the government when the total tax is greater than their total tax payments
To call for a review of an IRS decision or proposed adjustment.
Authorized IRS e-file Provider
A business authorized by the IRS to participate in the IRS e-file Program. The business may be a sole proprietorship, a partnership, a corporation, or an organization. Authorized IRS e-file Providers include Electronic Return Originators (EROs), Transmitters, Intermediate Service Providers, and Software Developers. These categories are not mutually exclusive. For example, an ERO can at the same time, be a Transmitter, a Software Developer, or an Intermediate Service Provider, depending on the function being performed.
B
A concept of tax fairness that states that people should pay taxes in proportion to the benefits they receive from government goods and services.
Compensation received by an employee for services performed. A bonus is given in addition to an employee’s usual compensation.
A continuous and regular activity that has income or profit as its primary purpose.
C
Assuming all other dependency tests are met, the citizen or resident test allows taxpayers to claim a dependency exemption for persons who are U.S. citizens for some part of the year or who live in the United States, Canada, or Mexico for some part of the year.
Compensation received by an employee for services performed. Commissions are paid based on a percentage of sales made or a fixed amount per sale.
An automatic tax collected from employers and employees to finance specific programs.
D
The result of the government taking in less money than it spends.
Amount that taxpayers can claim for a “qualifying child” or “qualifying relative”. Each exemption reduces the income subject to tax. The exemption amount is a set amount that changes from year to year. One exemption is allowed for each qualifying child or qualifying relative claimed as a dependent.
A qualifying child or qualifying relative, other than the taxpayer or spouse, who entitles the taxpayer to claim a dependency exemption.
This allows tax refunds to be deposited directly to the taxpayer’s bank account. Direct Deposit is a fast, simple, safe, secure way to get a tax refund. The taxpayer must have an established checking or savings account to qualify for Direct Deposit. A bank or financial institution will supply the required account and routing transit numbers to the taxpayer for Direct Deposit.
A tax that cannot be shifted to others, such as the federal income tax.
E
Includes wages, salaries, tips, includible in gross income, and net earnings from self-employment earnings.
A tax credit for certain people who work, meet certain requirements, and have earned income under a specified limit.
The transmission of tax information directly to the IRS using telephones or computers. Electronic filing options include (1) Online self-prepared using a personal computer and tax preparation software, or (2) using a tax professional. Electronic filing may take place at the taxpayer’s home, a volunteer site, the library, a financial institution, the workplace, malls and stores, or a tax professional’s place of business.
Electronic preparation means that tax preparation software and computers are used to complete tax returns. Electronic tax preparation helps to reduce errors.
Electronic Return Originator (ERO)
The Authorized IRS e-file Provider that originates the electronic submission of an income tax return to the IRS. EROs may originate the electronic submission of income tax returns they either prepared or collected from taxpayers. Some EROs charge a fee for submitting returns electronically.
Works for an employer. Employers can control when, where, and how the employee performs the work.
A tax on the sale or use of specific products or transactions.
Free from withholding of federal income tax. A person must meet certain income, tax liability, and dependency criteria. This does not exempt a person from other kinds of tax withholding, such as the Social Security tax.
Amount that taxpayers can claim for themselves, their spouses, and eligible dependents. There are two types of exemptions-personal and dependency. Each exemption reduces the income subject to tax. While each is worth the same amount, different rules apply to each.
F
A program sponsored by the IRS in partnership with participating states that allows taxpayers to file federal and state income tax returns electronically at the same time.
The federal government levies a tax on personal income. The federal income tax provides for national programs such as defense, foreign affairs, law enforcement, and interest on the national debt.
Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) Tax
Provides benefits for retired workers and their dependents as well as for disabled workers and their dependents. Also known as the Social Security tax.
To mail or otherwise transmit to an IRS service center the taxpayer’s information, in specified format, about income and tax liability. This information-the return-can be filed on paper, electronically (e-file).
Determines the rate at which income is taxed. The five filing statuses are: single, married filing a joint return, married filing a separate return, head of household, and qualifying widow(er) with dependent child.
Spending and income records and items to keep for tax purposes, including paycheck stubs, statements of interest or dividends earned, and records of gifts, tips, and bonuses. Spending records include canceled checks, cash register receipts, credit card statements, and rent receipts.
This is another term for a proportional tax.
formal tax legislation process
This is another term for a proportional tax.
Form W-4, Employee’s Withholding Allowance Certificate
Completed by the employee and used by the employer to determine the amount of income tax to withhold.
A foster child is any child placed with a taxpayer by an authorized placement agency or by court order. Eligible foster children may be claimed by taxpayers for tax benefits.
G
An excise tax paid by consumers when they purchase gasoline. The tax covers the manufacture, sale, and use of gasoline.
Money, goods, services, and property a person receives that must be reported on a tax return. Includes unemployment compensation and certain scholarships. It does not include welfare benefits and nontaxable Social Security benefits.
H
Head of Household filing status
You must meet the following requirements: 1. You are unmarried or considered unmarried on the last day of the year. 2. You paid more than half the cost of keeping up a home for the year. 3. A qualifying person lived with you in the home for more than half the year (except temporary absences, such as school). However, a dependent parent does not have to live with the taxpayer.
The concept that people in the same income group should be taxed at the same rate. “Equals should be taxed equally.”
I
Taxes on income, both earned (salaries, wages, tips, commissions) and unearned (interest, dividends). Income taxes can be levied on both individuals (personal income taxes) and businesses (business and corporate income taxes).
Performs services for others. The recipients of the services do not control the means or methods the independent contractor uses to accomplish the work. The recipients do control the results of the work; they decide whether the work is acceptable. Independent contractors are self-employed.
A tax that can be shifted to others, such as business property taxes.
A new or developing domestic industry whose costs of production are higher than those of established firms in the same industry in other countries.
***
***
The simultaneous increase of consumer prices and decrease in the value of money and credit.
informal tax legislation process
Individuals and interest groups expressing and promoting their opinions about tax legislation.
The charge for the use of borrowed money.
The income a person receives from certain bank accounts or from lending money to someone else.
Assists in processing tax return information between the ERO (or the taxpayer, in the case of online filing) and the Transmitter.
Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
The federal agency that collects income taxes in the United States.
Includes taxable and tax-exempt interest, dividends, capital gains net income, certain rent and royalty income, and net passive activity income.
Refers to the preparation and transmission of tax return information to the IRS using telephone lines or a computer with a modem or Internet access.
L
A person who represents the concerns or special interests of a particular group or organization in meetings with lawmakers. Lobbyists work to persuade lawmakers to change laws in the group’s favor.
long-distance telephone tax refund
Taxpayers are eligible to file for refunds of all excise tax they have paid on long-distance service billed to them after Feb. 28, 2003.
A tax paid on expensive goods and services considered by the government to be nonessential.
M
An economic system based on private enterprise that rests upon three basic freedoms: freedom of the consumer to choose among competing products and services, freedom of the producer to start or expand a business, and freedom of the worker to choose a job and employer.
Married Filing Joint filing status
You are married and both you and your spouse agree to file a joint return. (On a joint return, you report your combined income and deduct your combined allowable expenses.)
Married Filing Separate filing status
You must be married. This method may benefit you if you want to be responsible only for your own tax or if this method results in less tax than a joint return. If you and your spouse do not agree to file a joint return, you may have to use this filing status.
A broad tax that affects a majority of taxpayers.
Used to provide medical benefits for certain individuals when they reach age 65. Workers, retired workers, and the spouses of workers and retired workers are eligible to receive Medicare benefits upon reaching age 65.
N
When the amount of a credit is greater than the tax owed, taxpayers can only reduce their tax to zero; they cannot receive a “refund” for any excess nonrefundable credit.
A state’s refusal to recognize or obey a federal law.
payroll taxes
Include Social Security and Medicare taxes.
Can be claimed for the taxpayer and spouse. Each personal exemption reduces the income subject to tax by the exemption amount.
Personal Identification Number (PIN)
Allow taxpayers to “sign” their tax returns electronically. The PIN, a five-digit self-selected number, ensures that electronically submitted tax returns are authentic. Most taxpayers can qualify to use a PIN.
A tax that takes a larger percentage of income from high-income groups than from low-income groups.
Taxes on property, especially real estate, but also can be on boats, automobiles (often paid along with license fees), recreational vehicles, and business inventories.
A tax that takes the same percentage of income from all income groups.
A tax levied on imported goods with the purpose of reducing domestic consumption of foreign-produced goods.
Benefits that cannot be withheld from those who don’t pay for them, and benefits that may be “consumed” by one person without reducing the amount of the product available for others. Examples include national defense, streetlights, and roads and highways. Public services include welfare programs, law enforcement, and monitoring and regulating trade and the economy.
Q
To be a qualifying child, the dependent must meet eight tests: (1) relationship, (2) age, (3) residence, (4) support, (5) citizenship or residency, (6) joint return, (7) qualifying child of more than one person, and (8) dependent taxpayer.
There are tests that must be met to be a qualifying relative, they are: (1) not a qualifying child, (2) member of household or relationship, (3) citizenship or residency, (4) gross income, (5) support, (6) joint return, and (7) dependent taxpayer.
Qualifying Widow(er) filing status
If your spouse died in 2010, you can use married filing jointly as your filing status for 2010 if you otherwise qualify to use that status. The year of death is the last year for which you can file jointly with your deceased spouse. You may be eligible to use qualifying widow(er) with dependent child as your filing status for two years following the year of death of your spouse. For example, if your spouse died in 2010, and you have not remarried, you may be able to use this filing status for 2011 and 2012. This filing status entitles you to use joint return tax rates and the highest standard deduction amount (if you do not itemize deductions). This status does not entitle you to file a joint return.
R
Money owed to taxpayers when their total tax payments are greater than the total tax. Refunds are received from the government.
When the amount of a credit is greater than the tax owed, taxpayers can receive a “refund” for some of the unused credit.
A tax that takes a larger percentage of income from low-income groups than from high-income groups.
Factors needed to produce goods and services (natural, human, and capital goods).
The income the nation collects from taxes.
A tax on imported goods levied primarily to generate revenue for the federal government.
S
Compensation received by an employee for services performed. A salary is a fixed sum paid for a specific period of time worked, such as weekly or monthly.
A tax on retail products based on a set percentage of retail cost.
Self-employment income minus self-employment expenses, when self-employment income is less than self-employment expenses.
Self-employment income minus self-employment expenses, when self-employment income is greater than self-employment expenses.
Similar to Social Security and Medicare taxes. The self-employment tax rate is 15.3 percent of self-employment profit. The self-employment tax is calculated on Schedule SE—Self-Employment Tax. The self-employment tax is reported on Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return.
If on the last day of the year, you are unmarried or legally separated from your spouse under a divorce or separate maintenance decree and you do not qualify for another filing status.
A tax on goods such as tobacco and alcohol.
Provides benefits for retired workers and their dependents as well as for the disabled and their dependents. Also known as the Federal Insurance Contributions Act (FICA) tax.
Develops software for the purposes of (1) formatting electronic tax return information according to IRS specifications, and/or (2) transmitting electronic tax return information directly to the IRS.
Reduces the income subject to tax and varies depending on filing status, age, blindness, and dependency.
For dependency test purposes, support includes food, clothing, shelter, education, medical and dental care, recreation, and transportation. It also includes welfare, food stamps, and housing provided by the state. Support includes all income, taxable and nontaxable.
T
A tax on products imported from foreign countries.
Interest income that is subject to income tax. All interest income is taxable unless specifically excluded.
An action taken to lessen tax liability and maximize after-tax income.
The official body of tax laws and regulations.
A dollar-for-dollar reduction in the tax. Can be deducted directly from taxes owed.
A reduction in the amount of taxes taken by the government.
An amount (often a personal or business expense) that reduces income subject to tax.
Required payments of money to governments that are used to provide public goods and services for the benefit of the community as a whole.
A failure to pay or a deliberate underpayment of taxes.
Interest income that is not subject to income tax. Tax-exempt interest income is earned from bonds issued by states, cities, or counties and the District of Columbia.
A part of a person’s income on which no tax is imposed.
tax liability (or total tax bill)
The amount of tax that must be paid. Taxpayers meet (or pay) their federal income tax liability through withholding, estimated tax payments, and payments made with the tax forms they file with the government.
Computer software designed to complete tax returns. The tax preparation software works with the IRS electronic filing system.
The process that occurs when a tax that has been levied on one person or group is in fact paid by others.
Taxpayers are eligible to file for refunds of all excise tax they have paid on long-distance service billed to them after Feb. 28, 2003.
Money and goods received for services performed by food servers, baggage handlers, hairdressers, and others. Tips go beyond the stated amount of the bill and are given voluntarily.
Taxes on economic transactions, such as the sale of goods and services. These can be based on a set of percentages of the sales value (ad valorem-sales taxes), or they can be a set amount on physical quantities (“per unit”-gasoline taxes).
To send a tax return to the IRS electronically. Tax returns prepared on paper can be sent through the mail.
Sends the electronic return data directly to the IRS.
U
Money-making activities that people don’t report to the government, including both illegal and legal activities.
An excise tax, often in the form of a license or supplemental charge, levied to fund a public service.
A tax that is paid directly by the consumer of a good, product, or service.
V
The concept that people in different income groups should pay different rates of taxes or different percentages of their incomes as taxes. “Unequals should be taxed unequally.”
A system of compliance that relies on individual citizens to report their income freely and voluntarily, calculate their tax liability correctly, and file a tax return on time.
Volunteer Income Tax Assistance (VITA)
This provides free income tax return preparation for certain taxpayers. The VITA program assists taxpayers who have limited or moderate incomes, have limited English skills, or are elderly or disabled. Many VITA sites offer electronic preparation and transmission of income tax returns.
W
Compensation received by employees for services performed. Usually, wages are computed by multiplying an hourly pay rate by the number of hours worked.
withholding (“pay-as-you-earn” taxation)
Money, for example, that employers withhold from employees paychecks. This money is deposited for the government. (It will be credited against the employees’ tax liability when they file their returns.) Employers withhold money for federal income taxes, Social Security taxes and state and local income taxes in some states and localities.
***
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: Accounting, Financial Planning, Funding Basics, Glossary Terms, Investing, Marcinko Associates, Taxation | Tagged: accountant, accountants, CMA, CPA, EA, finance, Marcinko, personal-finance, tax, tax planning, tax terms, Taxation, taxes | Leave a comment »