How are Assets and Liabilities Related to Doctor Net Worth?

Dr. David E. Marcinko MBA
Before the relationship among financial assets, liabilities and net worth can be examined, some based definitions must be understood.
LINK: http://www.CertifiedMedicalPlanner.org
[A] Short-Term Assets
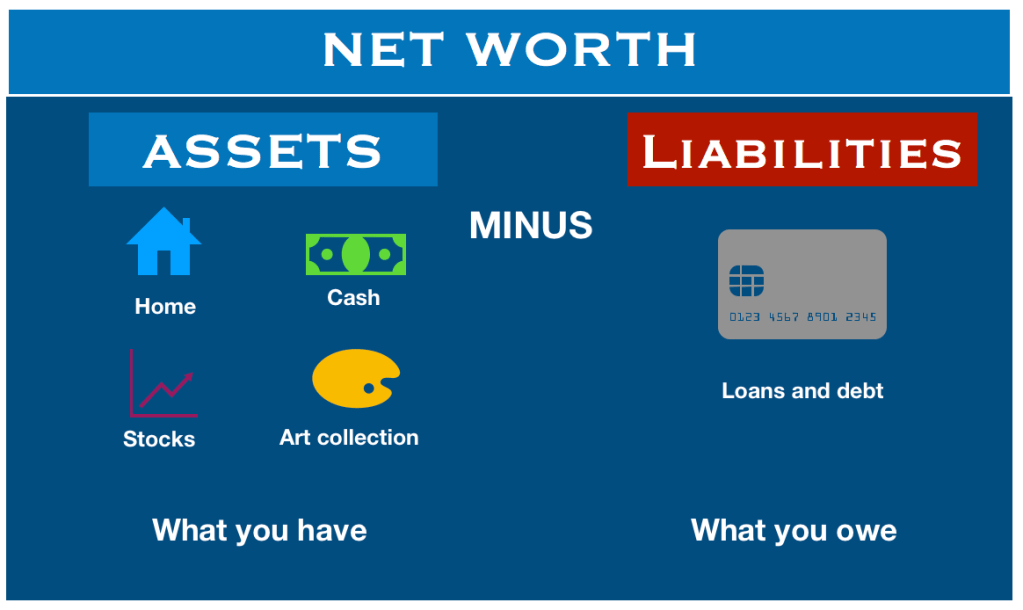
Short-term goals (less than 12 months) require liquidity or short-term assets. These assets include cash, checking and saving accounts, certificates of deposit, and money market accounts. These accounts have two things in common. The principal is guaranteed from risk of loss, and pay a very low interest rate. As an investment, they are considered substandard and one would only keep what is actually needed for liquidity purposes in these accounts.
[B] Long-Term Assets
Longer-term assets (more than 12 months) include real estate, mutual funds, retirement plans, stocks, and life insurance cash value policies. Bonds may also be an appropriate long-term investment asset for a number of reasons, for example, if you are seeking a regular and reliable stream of income or if you have no immediate need for the amount of the principal invested. Bonds also can be used to diversify your portfolio and reducing the overall risk that is inherent in stock investments.
[C] Short-Term Liabilities
Short-term liabilities (less than 12 months) include credit card debt, utility bills, and auto loans or leasing. When a young doctor leaves residency and starts practice, the foremost concern is student debt. This is an unsecured debt that is not backed by any collateral, except a promise to pay. There are recourses that an unsecured creditor can take to recoup the bad debt. Usually, if the unsecured creditor is successful obtaining a judgment, it can force wages to be garnished, and the Department of Education can withhold up to ten percent of a wages without first initiating a lawsuit, if in default. It is also probable that young medical professionals have been holding at least one credit card since their sophomore year in college. Credit card companies consider college student the most lucrative target market and medical students hold their first card for an average of fifteen years. There are several other types of other unsecured debt, including department store cards, professional fees, medical and dental bills, alimony, child support, rent; utility bills, personal loans from relatives, and health club dues, to name a few.
[D] Long-Term Liabilities
A secured debt, on the other hand, is debt that is pledged by a specific property. This is a collateralized loan. Generally, the purchased item is pledged with the proceeds of the loan. This would include long-term liabilities (more than 12 months) such as a mortgage, home equity loan, or a car loan. Although the creditor has the ability to take possession of your property in order to recover a bad debt, it is done very rarely. A creditor is more interested in recovering money. Sometimes, when borrowing money, there may be a requirement to pledge assets that are owned prior to the loan.
For example, a personal loan from a finance company requires that you pledge all personal property such as your car, furniture, and equipment. The same property may become subject to a judicial lien if you are sued and a judgment is made against you. In this case, you would not be able to sell or pledge these assets until the judgment is satisfied.
A common example of a lien would be from unpaid federal, state or local taxes. Doctors can be found personally liable for unpaid payroll taxes of employees in their professional corporations. Be aware that some assets and liabilities defy short or long-term definition. When this happens, simply be consistent in your comparison of financial statements, over time.
[E] Personal Physician Net Worth
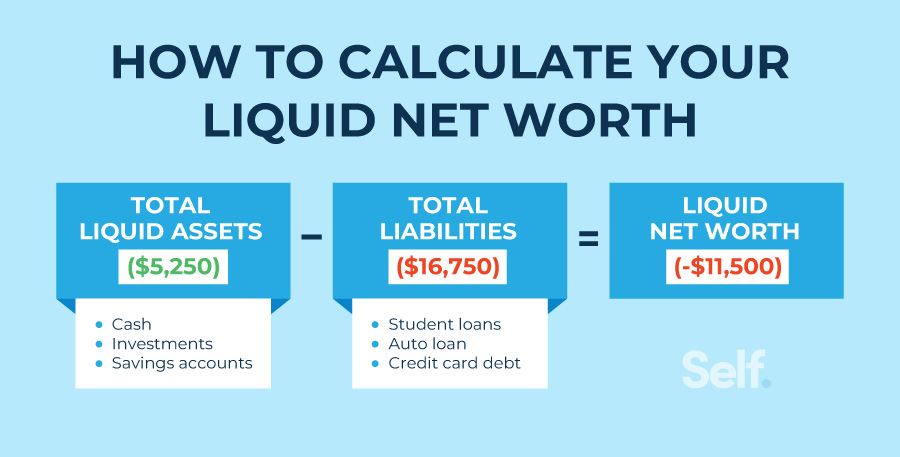
Once the value of all personal assets and liabilities is known, net worth can be determined with the following formula: Net worth = assets minus liabilities. Obviously, higher is better. In The Millionaire Next Door, Thomas H. Stanley, PhD, and William H. Danko give the following benchmark for net worth accumulation. Although conservative for physicians of a past generation, it may be more applicable in the future because of current managed care environment.
Here is the guide: Multiple your age by your annual pre-tax income from all sources – except inheritances – and divide by ten.
Real-Life Medical Example: As an HMO pediatrician, Dr. Curtis earned $ 60,000 last year. So, if she is 35, her net worth should be at least $ 210,000.
How do you get to that point? In a word, consume less, save more and watch the student loans. Stanley and Danko found that the typical millionaire set aside 15 percent of earned income annually and has enough invested to survive 10 years, at current income levels if he stopped working. Now, if Dr. Curtis lost her job tomorrow, how long could she pay herself the same salary?
[F] Common Liability Management Mistakes
A common liability management mistake is not recognizing when you are heading for trouble. If doctors are paying only the minimum payments on credit card debt, while continuing to charge purchases at a rate faster than the pay-down, trouble is brewing. If you don’t categorize your debt, you could find yourself paying down non-priority debt while ignoring priority debt.
A priority debt is one that is essential or subject to serious consequences, if not paid. Examples include rent, mortgage payments, utility bills, child support, car payments, unpaid taxes, and other secured debt. If in one month, a doctor had to choose between paying his accounting bill or his rent, it would be essential to pay the rent.
CITE: https://www.r2library.com/Resource/Title/082610254
Conclusion
Your thoughts and comments on this ME-P are appreciated. Feel free to review our top-left column, and top-right sidebar materials, links, URLs and related websites, too. Then, subscribe to the ME-P. It is fast, free and secure.
Speaker: If you need a moderator or speaker for an upcoming event, Dr. David E. Marcinko; MBA – Publisher-in-Chief of the Medical Executive-Post – is available for seminar or speaking engagements. Contact: MarcinkoAdvisors@msn.com
OUR OTHER PRINT BOOKS AND RELATED INFORMATION SOURCES: Invite Dr. Marcinko
Invite Dr. Marcinko
***
Filed under: "Advisors Only", "Doctors Only", Accounting, Career Development, CMP Program, Financial Planning, Funding Basics, Taxation, Touring with Marcinko | Tagged: Health Economics, long term assets, net worth, Physician assets, physician liabilities, physician net worth, shortterm assets | Leave a comment »