By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***
***
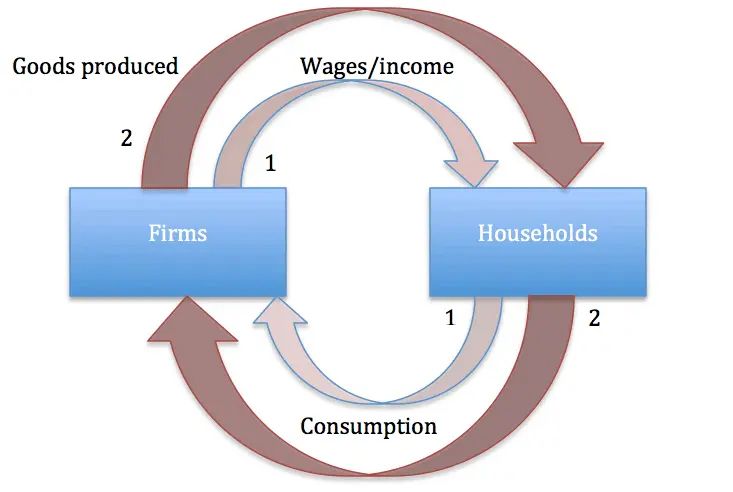
Say’s Law, named after the French economist Jean‑Baptiste Say, is a foundational idea in classical economics. Often summarized as “supply creates its own demand,” the law suggests that the act of producing goods and services inherently generates the income necessary to purchase them. This principle shaped economic thought throughout the 19th century and continues to influence debates about markets, government intervention, and the causes of economic crises.
Origins and Meaning Jean‑Baptiste Say introduced his law in the early 1800s in his Treatise on Political Economy. He argued that production is the source of demand: when producers create goods, they pay wages, rents, and profits, which in turn become purchasing power. In this view, general overproduction is impossible because every supply of goods corresponds to an equivalent demand. If imbalances occur, they are temporary and limited to specific sectors, not the economy as a whole.
Core Principles Say’s Law rests on several assumptions:
- Markets are self‑correcting: Any surplus in one area leads to adjustments in prices and production.
- Money is neutral: It serves only as a medium of exchange, not as a driver of demand.
- Production drives prosperity: Economic growth depends on increasing output, not stimulating consumption.
- No long‑term unemployment: Since supply creates demand, workers displaced in one industry will eventually find employment elsewhere.
These ideas aligned with classical economists’ belief in minimal government intervention and the efficiency of free markets.
Influence on Classical Economics Say’s Law became a cornerstone of classical economics, reinforcing the belief that recessions or depressions were temporary and self‑correcting. Economists like David Ricardo and John Stuart Mill adopted versions of the law, using it to argue against policies aimed at stimulating demand. The law supported laissez‑faire approaches, suggesting that governments should avoid interfering with markets, as production itself would ensure economic balance.
Criticism and Keynesian Revolution Say’s Law faced its greatest challenge during the Great Depression of the 1930s. Widespread unemployment and idle factories contradicted the idea that supply automatically generates demand. John Maynard Keynes famously rejected Say’s Law in his General Theory of Employment, Interest, and Money (1936). Keynes argued that demand, not supply, drives economic activity. He showed that insufficient aggregate demand could lead to prolonged recessions, requiring government intervention through fiscal and monetary policies.
Keynes’s critique marked a turning point in economics. While Say’s Law emphasized production, Keynesian economics highlighted consumption and demand management. This shift reshaped economic policy, leading to active government roles in stabilizing economies.
Modern Perspectives Today, Say’s Law is not accepted in its original form, but elements of it remain relevant. Supply‑side economists, for example, argue that policies encouraging production—such as tax cuts and deregulation—can stimulate growth. In contrast, Keynesians stress the importance of demand management. The debate reflects a broader tension in economics: whether prosperity depends more on producing goods or ensuring people have the means and willingness to buy them.
Conclusion: Say’s Law was a bold attempt to explain the self‑sustaining nature of markets. While its claim that “supply creates its own demand” proved too simplistic in the face of modern economic realities, it remains a vital part of the history of economic thought. The controversy surrounding Say’s Law highlights the evolving nature of economics, where theories are tested against real‑world crises and adapted to new circumstances. Even today, discussions of supply‑side versus demand‑side policies echo the enduring influence of Say’s original insight.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", economics, finance, Glossary Terms, Health Economics, Investing, Marcinko Associates, Touring with Marcinko | Tagged: classical economics, consumption, david marcino, demand-supply, depression, economic, economics, economy, finance, Income, Keynes, money, politics, Say's law, supply-demand, wages | Leave a comment »