By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***
***
Understanding the Differences Between Microeconomics and Macroeconomics
Economics is the study of how societies allocate scarce resources to meet the needs and wants of individuals. It is broadly divided into two main branches: microeconomics and macroeconomics. While both aim to understand economic behavior and decision-making, they differ significantly in scope, focus, and application. Understanding these differences is essential for grasping how economies function at both individual and national levels.
2025 Nobel: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2025/10/14/nobel-prize-economics-2025/
Microeconomics: The Study of Individual Units
Microeconomics focuses on the behavior of individual economic agents—such as consumers, firms, and households—and how they make decisions regarding resource allocation. It examines how these entities interact in specific markets, how prices are determined, and how supply and demand influence economic outcomes.
Key concepts in microeconomics include:
- Demand and Supply: Microeconomics analyzes how the quantity of goods demanded by consumers and the quantity supplied by producers interact to determine market prices.
- Elasticity: This measures how responsive demand or supply is to changes in price or income.
- Consumer Behavior: Microeconomics studies how individuals make choices based on preferences, budget constraints, and utility maximization.
- Production and Costs: It explores how firms decide on the optimal level of output and the costs associated with production.
- Market Structures: Microeconomics categorizes markets into perfect competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly, each with distinct characteristics and implications for pricing and output.
Microeconomic analysis is crucial for understanding how specific sectors operate, how businesses strategize, and how consumers respond to changes in prices or income. For example, a company might use microeconomic principles to determine the price point that maximizes profit or to assess the impact of a new competitor entering the market.
Macroeconomics: The Study of the Economy as a Whole
Macroeconomics, on the other hand, deals with the performance, structure, and behavior of an entire economy. It looks at aggregate indicators and phenomena, such as national income, unemployment, inflation, and economic growth. Macroeconomics seeks to understand how the economy functions at a broad level and how government policies can influence economic outcomes.
Key areas of macroeconomics include:
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP): This measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country and serves as a key indicator of economic health.
- Unemployment: Macroeconomics examines the causes and consequences of unemployment and the effectiveness of policies aimed at reducing it.
- Inflation and Deflation: It studies changes in the general price level and their impact on purchasing power and economic stability.
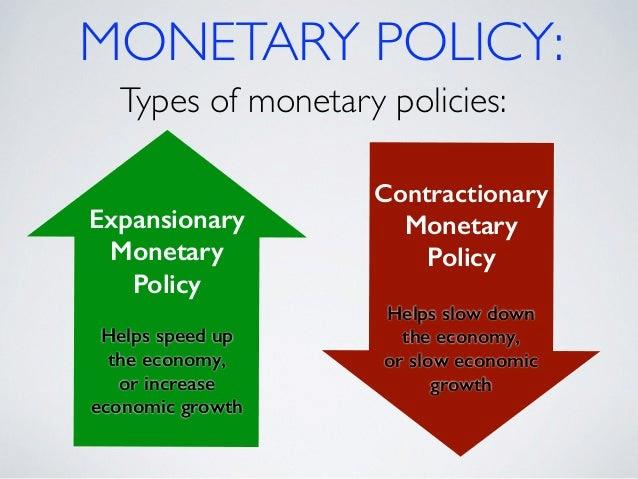
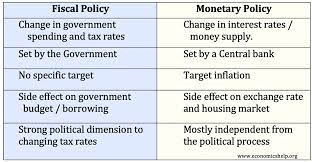
- Fiscal and Monetary Policy: Macroeconomics evaluates how government spending, taxation, and central bank actions influence economic activity.
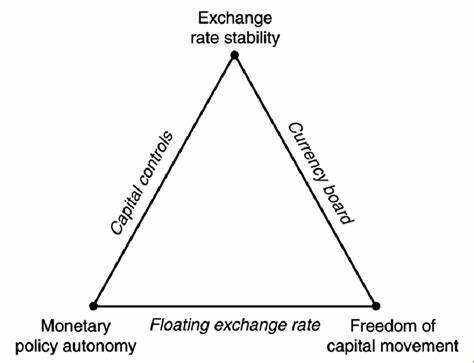
- International Trade and Finance: It explores exchange rates, trade balances, and the impact of globalization on national economies.
Macroeconomic analysis is essential for policymakers, economists, and financial institutions. For instance, central banks use macroeconomic data to set interest rates, while governments design fiscal policies to stimulate growth or curb inflation.
Interdependence Between Micro and Macro
Despite their differences, microeconomics and macroeconomics are deeply interconnected. Micro-level decisions collectively shape macroeconomic outcomes. For example, widespread consumer spending boosts aggregate demand, influencing GDP and employment levels. Conversely, macroeconomic conditions—such as inflation or interest rates—affect individual behavior. A rise in interest rates may discourage borrowing and reduce consumer spending, impacting businesses at the micro level.
Economists often use insights from both branches to develop comprehensive models and forecasts. For instance, understanding consumer behavior (micro) helps predict changes in aggregate consumption (macro), which in turn informs policy decisions.
Austrian Economics: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2025/10/11/keynesian-versus-austrian-economics/
Conclusion
Microeconomics and macroeconomics offer distinct yet complementary perspectives on economic activity. Microeconomics provides a granular view of individual decision-making and market dynamics, while macroeconomics offers a broader understanding of national and global economic trends. Together, they form the foundation of economic theory and practice, guiding businesses, governments, and individuals in making informed decisions.
A well-rounded grasp of both branches is essential for anyone seeking to understand how economies function and evolve in an increasingly complex world.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: economics, finance, Glossary Terms, Health Economics, Marcinko Associates | Tagged: david marcinko, economics, economy, finance, fiscal policy, GDP, Health Economics, inflation, macro economics, micro economics, monetary policy, nobel economics, politics, trilemma economics | Leave a comment »