By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***
***
In the realm of finance and investment, the pursuit of profit is inseparable from the presence of risk. Every investor, whether an individual or an institution, must grapple with the reality that higher returns often come with greater uncertainty. To evaluate investments effectively, it is not enough to look at raw returns alone. Instead, one must consider how much risk was undertaken to achieve those returns. This balance is captured by the concept of the risk-adjusted rate of return, a cornerstone of modern portfolio theory and investment analysis.
The risk-adjusted rate of return measures the profitability of an investment relative to the risk assumed. Unlike simple return calculations, which only show the percentage gain or loss, risk-adjusted metrics incorporate volatility and other forms of uncertainty. For example, two investments may both yield a 10% annual return, but if one is highly volatile and the other is stable, the stable investment is more attractive when viewed through a risk-adjusted lens. This approach ensures that investors are not misled by high returns that are achieved through excessive risk-taking.
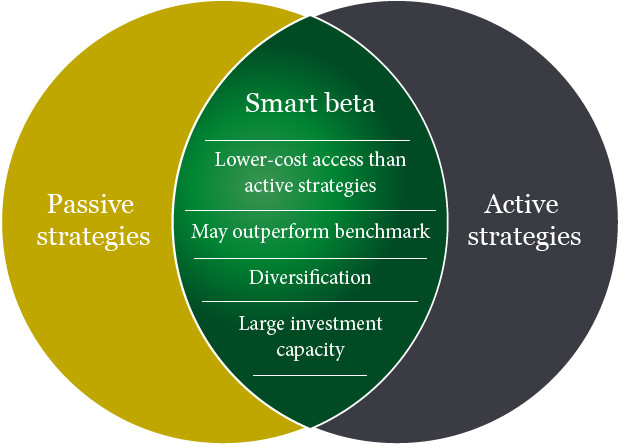
Several tools have been developed to calculate risk-adjusted returns. The Sharpe Ratio is among the most widely used. It measures excess return per unit of risk, with risk defined as the standard deviation of returns. A higher Sharpe Ratio indicates that an investment is delivering better returns for the level of risk taken. Another measure, the Treynor Ratio, evaluates returns relative to systematic risk, using beta as the risk measure. The Sortino Ratio refines the Sharpe Ratio by focusing only on downside volatility, thereby distinguishing between harmful risk and general fluctuations. Each of these metrics provides a different perspective, but all share the same goal: to assess whether the reward justifies the risk.
The importance of risk-adjusted returns extends beyond individual securities to entire portfolios. Portfolio managers use these metrics to compare strategies, evaluate asset allocations, and determine whether their investment approach aligns with client objectives. For instance, a hedge fund may report impressive raw returns, but if those returns are accompanied by extreme volatility, its risk-adjusted performance may be inferior to that of a conservative mutual fund. By incorporating risk-adjusted measures, investors can make more informed decisions and build portfolios that reflect their risk tolerance and long-term goals.
Risk-adjusted returns also play a vital role in distinguishing skill from luck in investment management. A manager who consistently delivers high risk-adjusted returns demonstrates genuine expertise in navigating markets. Conversely, a manager who achieves high raw returns through excessive risk-taking may simply be gambling with investor capital. This distinction is critical for institutions and individuals alike, as it ensures that performance evaluations are grounded in sustainability rather than short-term speculation.
Of course, risk-adjusted metrics are not without limitations. They often rely on historical data, which may not accurately predict future outcomes. Market conditions can change rapidly, and past volatility may not reflect future risks. Additionally, different metrics may yield conflicting results, complicating the decision-making process. Despite these challenges, risk-adjusted returns remain indispensable because they encourage investors to look beyond superficial gains and consider the broader context of risk management.
In conclusion, the risk-adjusted rate of return is a fundamental concept in investment analysis. By integrating both risk and reward into a single measure, it empowers investors to evaluate opportunities more effectively, compare diverse assets, and build resilient portfolios. While no metric is flawless, the emphasis on risk-adjusted performance ensures that investment decisions are not driven solely by the pursuit of high returns but by the pursuit of sustainable, well-balanced growth. In a financial landscape defined by uncertainty, the ability to measure success in terms of both profit and prudence is what ultimately separates wise investing from reckless speculation.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", finance, Financial Planning, Interviews, Portfolio Management, Touring with Marcinko | Tagged: david marcinko, finance, Investing, investment, Modern Portfolio Theory, MPT, personal-finance, Portfolio Management, portfolio theory, Sharpe Ratio, stocks, Treynor Ratio | Leave a comment »