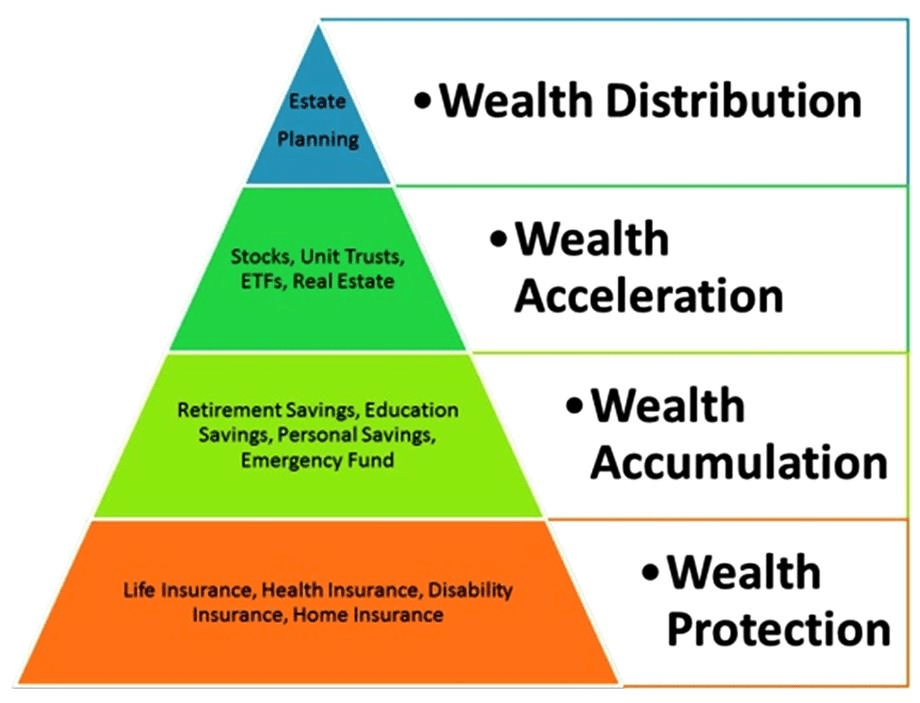
By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***

***
SPONSOR: http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
The U.S. faces a heightened risk of recession in 2026, with economic indicators, expert forecasts, and global instability contributing to widespread concern. While some analysts remain cautiously optimistic, the probability of a downturn is significant.
The potential for a U.S. recession in 2026 is a topic of growing concern among economists, policymakers, and investors. According to UBS, the probability of a recession has surged to 93% based on hard data analysis, including employment trends, industrial production, and credit market signals. This alarming figure reflects a convergence of economic stressors that could culminate in a downturn by the end of 2026.
One of the most prominent warning signs is the inverted yield curve, a historically reliable predictor of recessions. When short-term interest rates exceed long-term rates, it suggests that investors expect weaker growth ahead. This inversion, coupled with elevated federal debt and persistent inflationary pressures, has led many analysts to forecast a slowdown in consumer spending and business investment.
Despite these concerns, some sectors—particularly artificial intelligence (AI)—are providing temporary buoyancy. The AI infrastructure boom has fueled GDP growth and market optimism, with global AI investment projected to reach $500 billion by 2026.
However, experts warn that this surge may be masking underlying economic fragility. If AI-driven investment slows, the economy could quickly lose momentum, revealing vulnerabilities in other sectors such as manufacturing and retail.
Global factors also play a critical role. Trade tensions, geopolitical instability, and fluctuating oil prices have created an unpredictable environment. The lingering effects of tariff pass-throughs and policy uncertainty are expected to intensify in 2026, further straining the U.S. economy. Additionally, speculative forecasts—like those from mystic Baba Vanga—have captured public imagination by predicting a “cash crush” that could disrupt both virtual and physical currency systems, although such claims lack empirical support. Not all forecasts are dire. Oxford Economics suggests that while growth will moderate, the U.S. may avoid a full-blown recession thanks to continued investment incentives and robust AI-related spending. Their above-consensus GDP forecast hinges on the assumption that business confidence remains stable and that fiscal policy supports non-AI sectors effectively.
Nevertheless, the risks are real and multifaceted. The Polymarket prediction platform currently estimates a 43% chance of a U.S. recession by the end of 2026, based on criteria such as two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth or an official declaration by the National Bureau of Economic Research.
In conclusion, while the U.S. economy may continue to navigate “choppy waters,” the potential for a recession in 2026 is substantial. Policymakers must remain vigilant, balancing stimulus with fiscal discipline, and addressing structural weaknesses before temporary growth drivers fade.
The coming year will be pivotal in determining whether the U.S. can steer clear of recession or succumb to the mounting pressures.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", economics, finance, Funding Basics, Glossary Terms, Investing, Portfolio Management | Tagged: AI, artificial heart, artificial intelligence, Baba Vanga, economics, economy, finance, GDP, Inverted yield curve, Investing, National Bureau Economic Research, NBER, Oxford economics, recession, UBS | Leave a comment »