“Correlation” has been used over the past twenty years by institutions, [physician] investors and financial advisors to assemble portfolios of moderate INVESTMENT risk
By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd CMP®
SPONSOR: http://www.CertifiedMedicalPlanner.org
Modern Portfolio Theory approaches investing by examining the complete market and the full economy. MPT places a great emphasis on the correlation between investments.
DEFINITION: Correlation is a measure of how frequently one event tends to happen when another event happens. High positive correlation means two events usually happen together – high SAT scores and getting through college for instance. High negative correlation means two events tend not to happen together – high SATs and a poor grade record. No correlation means the two events are independent of one another.
CITATION: https://www.r2library.com/Resource/Title/0826102549
CORRELATION: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2021/02/05/correlation-is-not-causation/
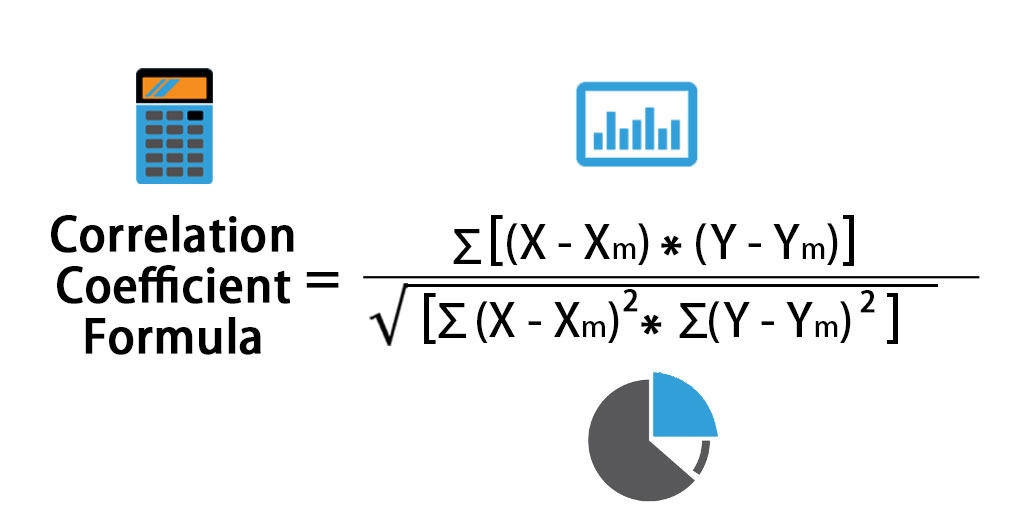
In statistical terms two events that are perfectly correlated have a “correlation coefficient” of 1; two events that are perfectly negatively correlated have a correlation coefficient of -1; and two events that have zero correlation have a coefficient of 0.
In calculating correlation, a statistician would examine the possibility of two events happening together, namely:
- If the probability of A happening is 1/X;
- And the probability of B happening is 1/Y; then
- The probability of A and B happening together is (1/X) times (1/Y), or 1/(X times Y).
There are several laws of correlation including;
- Combining assets with a perfect positive correlation offers no reduction in portfolio risk. These two assets will simply move in tandem with each other.
- Combining assets with zero correlation (statistically independent) reduces the risk of the portfolio. If more assets with uncorrelated returns are added to the portfolio, significant risk reduction can be achieved.
- Combing assets with a perfect negative correlation could eliminate risk entirely. This is the principle with “hedging strategies”. These strategies are discussed later in the book.
In the real world, negative correlations are very rare. Most assets maintain a positive correlation with each other. The goal of a prudent investor is to assemble a portfolio that contains uncorrelated assets. When a portfolio contains assets that possess low correlations, the upward movement of one asset class will help offset the downward movement of another. This is especially important when economic and market conditions change.
As a result, including assets in your portfolio that are not highly correlated will reduce the overall volatility (as measured by standard deviation) and may also increase long-term investment returns. This is the primary argument for including dissimilar asset classes in your portfolio. Keep in mind that this type of diversification does not guarantee you will avoid a loss. It simply minimizes the chance of loss.
In this table provided by Ibbotson, the average correlation between the five major asset classes is displayed. The lowest correlation is between the U.S. Treasury Bonds and the EAFE (international stocks). The highest correlation is between the S&P 500 and the EAFE; 0.77 or 77 percent. This signifies a prominent level of correlation that has grown even larger during this decade. Low correlations within the table appear most with U.S. Treasury Bills.
Historical Correlation of Asset Classes
Benchmark 1 2 3 4 5 6
1 U.S. Treasury Bill 1.00
2 U.S. Bonds 0.73 1.00
3 S&P 500 0.03 0.34 1.00
4 Commodities 0.15 0.04 0.08 1.00
5 International Stocks -0.13 -0.31 0.77 0.14 1.00
6 Real Estate 0.11 0.43 0.81 -0.02 0.66 1.00
Table Source: Ibbotson 1980-2012
ASSESSMENT: Your thoughts are appreciated.
ORDER Textbook: https://www.amazon.com/Comprehensive-Financial-Planning-Strategies-Advisors/dp/1482240289/ref=sr_1_1?ie=UTF8&qid=1418580820&sr=8-1&keywords=david+marcinko
SECOND OPINIONS: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/schedule-a-consultation/
INVITE DR. MARCINKO: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/dr-david-marcinkos-bookings/
THANK YOU
***
Filed under: Glossary Terms, Investing, Marcinko Associates | Tagged: causation, correlation, David Edward Marcinko, Investing Basics, Modern Portfolio Theory, MPT | Leave a comment »