By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***
***
SPONSOR: http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
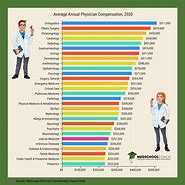
A growing number of surveys measure physician compensation, encompassing a varying depth of analysis. Physician compensation data, divided by specialty and subspecialty, is central to a range of consulting activities including practice assessments and valuations of healthcare enterprises. The AMA maintains the most comprehensive database of information on physicians in the U.S., with information on over 940,000 physicians and residents, and 77,000 medical students. Started in 1906, the AMA “Physician Masterfile,” which contains information on physician education, training, and professional certification information, is updated annually through the Physicians’ Professional Activities questionnaire and the collection and validation efforts of AMA’s Division of Survey and Data Resources (SDR). A selection of other sources of healthcare related compensation and cost data is set forth below.
“Physician Characteristics and Distribution in the U.S.” is an annual survey based on a variety of demographic information from the Physician Masterfile dating back to 1963. It includes detailed information regarding trends, distribution, and professional and individual characteristics of the physician workforce.
“Physician Socioeconomic Statistics”, published from 2000 to 2003, was a result of the merger between two prior AMA annuals: (1) “Socioeconomic Characteristics of Medical Practice”; and, (2) “Physician Marketplace Statistics.” Data has compiled from a random sampling of physicians from the Physician Masterfile into what is known as the Socioeconomic Monitoring System, which includes physician age profiles, practice statistics, utilization, physician fees, professional expenses, physician compensation, revenue distribution by payor, and managed care contracts, among other categories.
The Medical Group Management Association’s (MGMA) “Physician Compensation and Production Survey” is one of the largest in the U.S. with approximately 3,000 group practices responding as of the 2023 edition publication. Data is provided on compensation and production for 125 specialties. The survey data are also published on CD by John Wiley & Sons ValueSource; the additional details available in this media provide better bench marking capabilities.
The MGMA’s “Cost Survey” is one of the best known surveys of group practice income and expense data, having been published in some form since 1955, and obtaining over 1,600 respondents, combined, for the 2008 surveys: “Cost Survey for Single Specialty Practices” and “Cost Survey for Multispecialty Practices.” Data is provided for a detailed listing of expense categories and is also calculated as a percentage of revenue and per FTE physician, FTE provider, patient, square foot, and Relative Value Unit (RVU). The survey provides information on multispecialty practices by performance ranking, geographic region, legal organization, size of practice, and percent of capitated revenue. Detailed income and expense data is provided for single specialty practice in over 50 different specialties and subspecialties.
The “Medical Group Financial Operations Survey” was created through a partnership between RSM McGladrey and the American Medical Group Association (AMGA), and provides benchmark data on support staff and physician salaries, physician salaries, staffing profiles and benefits, and other financial indicators. Data is reported as a percent of managed care revenues, per full-time physician, and per square foot, and is subdivided by specialty mix, capitation level, and geographic region with detailed summaries of single specialty practices in several specialties.
“Statistics: Medical and Dental Income and Expense Averages” is an annual survey produced by the National Society of Certified Healthcare Business Consultants (NSCHBC), formerly known as the National Association of Healthcare Consultants (NAHC), and the Academy of Dental CPAs. It has been published annually for a number of years and the “2023 Report Based on 2022 Data” included detailed income and expense data from over 2,700 practices and 4,900 physicians in 62 specialties.
***
***
Medical Specialty Trends
The characteristics of both the practice and the profitability of different physician specialties vary greatly. Information on trends affecting specific specialties should further refine the types of industry information gathered including changes in treatment, technology, competition, reimbursement, and the regulatory environment. For many of the subspecialties, oversupply and under supply issues and the corresponding demand and compensation trends are central to the analysis of potential future earnings and the value of established medical entities. Information that is available and that may be gathered can range from broad practice overviews to, for example, specific procedural utilization demand and forecasts for a precise local geographic area.
A large number of national and state medical associations and organizations gather and produce information on these various aspects of the practice of different individual physician specialties and subspecialties. Information may be found in trade press articles, medical specialty associations and their publications, national surveys, specialty accreditation bodies, governmental reports and studies, and elsewhere. The American Medical Association’s (AMA) as well as the MGMA both publish comprehensive physician practice survey information.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
***
***
Filed under: "Doctors Only", Accounting, Ask a Doctor, curated experts,, Funding Basics, Health Economics, Healthcare Finance, Marcinko Associates | Tagged: AMA, american medical association, Art, books, Cost Survey for Multispecialty Practices, david marcinko, Division of Survey and Data Resources, DO, doctor, doctor compensation data sources, doctor salary, DPM, lifestyle, MD, MGMA, National Society of Certified Healthcare Business Consultants, physician compensation, physician compensation data soures, physician salary, relative value uniuts, RVUs, travel | Leave a comment »