By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***
***
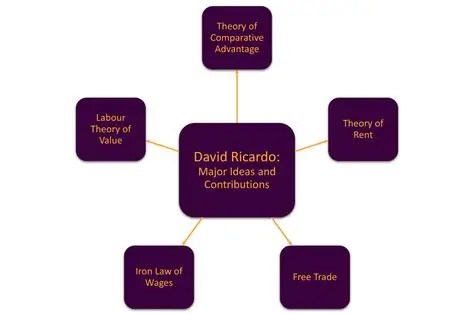
Ricardian economics, rooted in the theories of 19th-century economist David Ricardo, emphasizes comparative advantage, free trade, and the neutrality of government debt—most notably through the concept of Ricardian equivalence. While these ideas have shaped macroeconomic thought, their relevance to medicine and healthcare policy is less direct. Still, exploring Ricardian principles offers a provocative lens through which to examine the fiscal sustainability and efficiency of modern healthcare systems.
At the heart of Ricardian equivalence is the idea that consumers are forward-looking and internalize government budget constraints. If a government finances healthcare through debt rather than taxes, rational agents will anticipate future tax burdens and adjust their behavior accordingly. In theory, this undermines the effectiveness of deficit-financed healthcare spending as a stimulus. Applied to medicine, this suggests that long-term fiscal responsibility is crucial: expanding healthcare access through borrowing may not yield the intended economic or health benefits if citizens expect future costs to rise.
This insight could inform debates on healthcare reform, especially in countries grappling with ballooning medical expenditures. Ricardian economics warns against short-term fixes that ignore long-term fiscal implications. For example, expanding public insurance programs without sustainable funding mechanisms could lead to intergenerational inequities and economic distortions. Policymakers might instead focus on reforms that align incentives, reduce waste, and promote cost-effective care—principles that resonate with Ricardo’s emphasis on efficiency and comparative advantage.
***
***
However, Ricardian economics offers limited guidance on the unique moral and practical dimensions of medicine. Healthcare is not a typical market good. Patients often lack the information or autonomy to make rational choices, especially in emergencies. Moreover, the sector is rife with externalities: one person’s vaccination benefits the broader community, and untreated illness can strain public resources. These complexities challenge the assumption of rational, forward-looking behavior central to Ricardian equivalence.
Additionally, Ricardo’s theory of comparative advantage—where nations benefit by specializing in goods they produce most efficiently—has implications for global health. It supports international collaboration in pharmaceutical production, medical research, and telemedicine. Yet, over-reliance on global supply chains can expose vulnerabilities, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic when countries faced shortages of critical medical supplies.
In conclusion, Ricardian economics provides valuable fiscal insights that can inform healthcare policy, particularly regarding debt sustainability and efficient resource allocation. Its emphasis on long-term planning and comparative advantage can guide reforms that make medicine more resilient and cost-effective. However, the theory’s assumptions about rational behavior and market dynamics limit its applicability to the nuanced realities of healthcare. Medicine requires not just economic efficiency but ethical considerations, equity, and compassion—areas where Ricardian economics falls short. Thus, while it can contribute to the conversation, it cannot “save” medicine alone.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", Ask a Doctor, economics, Glossary Terms, Health Economics, Health Insurance, Healthcare Finance, Insurance Matters | Tagged: david marcinko, david ricardo, DO, doctors, DPM, economics, economy, finance, healthcare, macro-economics, MD, medicine, Population Health, public health, Ricardian economics | Leave a comment »