SPONSOR: http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
***
By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd CMP™
WHAT YOU “MUST KNOW“ ABOUT FINANCIAL ADVISORY FEES
Investment fees still matter despite dropping dramatically over the past several decades due to computer automation, algorithms and artificial intelligence, etc. And, they can make a big difference to your financial health. So, before buying any investment, it’s vital to uncover all real financial advisor and stock broker costs.
HEDGE FUND FEES: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2025/04/18/stocks-basic-definitions/
SIX TYPES OF FEES AND EXPENSES
1. Up-front salesperson commissions. It is easy to ask; “If I buy this investment today and want to get out tomorrow, how much money do I get back?” If the answer is not “all your money,” the difference is probably upfront fees and commissions. These fees may run as high as 30% of the money invested. If you were to earn 5% a year on the investment, it would take 8 years just to break even.
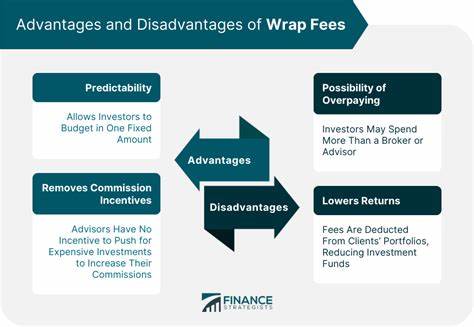
2. Ongoing advisory fees. These are monthly, quarterly, or annual fees paid to advisors for their investment advice and oversight. This includes working with you to pick the asset classes, set diversification, select a portfolio manager, optimize taxes, re-balance holdings and other periodic tasks.
These fees have many names including wrap fee or investment advisory fees. The normal “rule of thumb” is 1% of assets managed, although fees can range from 0 to 7%. Today, it can even be as low as .5%. It can be charged even if the advisor receives an upfront commission. It can be easy to see, or hidden in the fine print.
3. Additional service fees. Find out specifically what services are included financial advisory fees. Additional fees for financial planning or other services are rarely disclosed. They can range from minimal hand-holding focused on your investments to comprehensive financial planning.
4. Ongoing managerial expense ratio fees. These are incredibly well hidden that you may not see them in your statements or invoices. The only way to know is to read the prospectus or other third party analysis, like Morningstar.com. And, they can vary greatly for the same investment, depending on the class of share you buy.
For example, American Fund’s New Perspective Fund’s expense ratio ranges from 0.45% to 1.54%. The average expense ratio of a mutual fund that invests in stocks is 1.35%. Conversely, the average expense ratio of a Vanguard S&P 500 Fund is 0.10%. The difference of 1.25% is staggering over time.
5. Miscellaneous fees. Some advisors charge $50 – $100 a year per account to open or close an account, and even fees to dollar cost average your funds into the market.
6. Transaction fees. Every time you buy or sell a fund, a fee is typically paid to a custodian. These can range from $5 to hundreds of dollars per transaction.
7. Fee Only: Paid directly by clients for their services and can’t receive other sources of compensation, such as payments from fund providers. Act as a fiduciary, meaning they are obligated to put their clients’ interests first
8. Fee Based: Paid by clients but also via other sources, such as commissions from financial products that clients purchase. Brokers and dealers (or registered representatives) are simply required to sell products that are “suitable” for their clients.
A “suitable” investment is defined by FINRA as one that fits the level of risk that an investor is willing and able, as measured by personal financial circumstances, to take on. The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority is a private American corporation that acts as a Self Regulatory Organization (SRO) that regulates member stock brokerage firms and exchange markets. These criteria must be met. It is not enough to state that an investor has a risk-friendly investment profile. In addition, they must be in a financial position to take certain chances with their money. It is also necessary for them to
A hedge fund is a limited partnership of private investors whose money is managed by professional fund managers who use a wide range of strategies; including leveraging [debt] or trading of non-traditional assets [real-estate, collectible, commodities, cyrpto-currency, etc] to earn above-average returns. Hedge funds are considered a risky alternative investment and usually require a high minimum investment or net worth. This person is known as an “accredited investor” or “Regulation D” investor by the US Securities Exchange Commission and must have the following attributes:
- A net worth, combined with spouse, of over $1 million, not including primary residence
- An income of over $200,000 individually, or $300,000 with a spouse, in each of the past two years
Not a fiduciary.
Ways to minimize fees
Choose the fee structure. The fee structure should align with your needs. Consider the type of advice you seek, the number of times needed and the complexity of your financial situation. You can always negotiating tactics are free to ask for a better deal.
Compare fees. It is essential to research and compare different fees. Be sure to read the fine print for details or costs that are not a base fee.
Robo-advisors: For simple investment goals, with little specificity, robo-advisors may be a cost-effective option. They charge lower fees than conventional financial advisors and provide an automated, algorithmic approach to managing your investments.
Assessment
The average cost of working with a human financial advisor in 2024 was 0.5% to 2.0% of assets managed, $200 to $400 per hourly consultation, a flat fee of $1,000 to $3,000 for a one-time service, and/or a 3% to 6% commission fee on the product types sold.
ADVISORY FEES: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2025/02/26/be-aware-financial-advisory-fees-fee-based-versus-fee-only/
Conclusion
When ruminating over financial advisory fees; read and understand the contract with disclosures, do not sign a confidentiality or non-disclosure agreement, and do not waive your right to a lawsuit. According to colleague Dr. Charles F. Fenton IIII JD, forced legal settlements almost always favor the advisor over the client.
References and Readings:
1. https://www.capitalgroup.com [American Funds]
2. Marcinko, DE and Hetico, HR; Comprehensive Financial Planning Strategies for Doctors and Advisors [Best Practices from Leading Consultants and Certified Medical Planners™] Productivity Press, New York, 2017.
3. Marcinko, DE: Dictionary of Health Economics and Finance. Springer Publishing Company, NY 2006
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit a RFP for speaking engagements: MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
Refer, Like and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", Alternative Investments, CMP Program, Experts Invited, Financial Planning, Glossary Terms, Investing, Marcinko Associates, Portfolio Management | Tagged: advisory fees, agents, CMP, commissions, expenses, fee based, fee bases, fee only, fiduciary, finance, FINRA, hedge fund, Investing, managerial fees, personal-finance, portfolio manager, Regulation D, robo advisors, SEC, stock brokers, suitability | Leave a comment »