LEADERSHIP versus MANAGEMENT
***
***
By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
By Professor Gary A. Cook PhD
By Professor Eugene Schmuckler PhD MBA MEd CTS
Many of us have encountered a person who may intellectually be at upper levels, but whose ability to interact with others appears to that of one who is highly immature. This is the individual who is prone to becoming angry easily, verbally attacks co-workers, is perceived as lacking in compassion and empathy, and cannot understand why it is difficult to get others to cooperate with them and their agendas.
THINK: Sheldon Cooper PhD D.Sc MA BA of the The Big Bank Theory TV show.
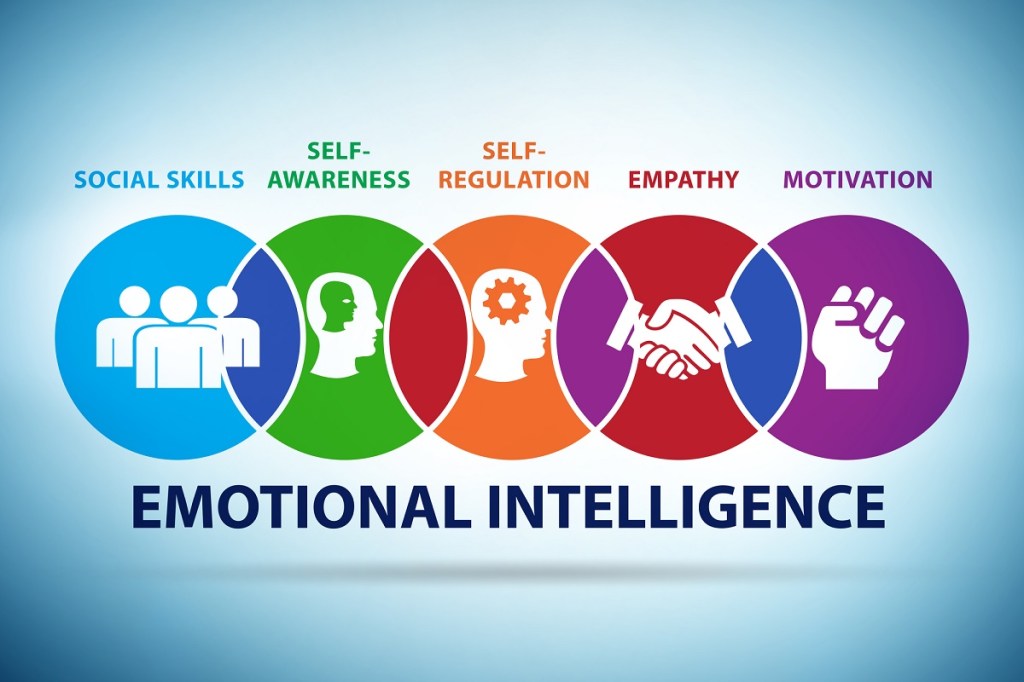
The concept of Emotional Intelligence [EQ] was brought into the public domain when Daniel Goleman authored a book entitled, Emotional Intelligence.” According to Goleman, emotional intelligence consists of four basic non-cognitive competencies: self awareness, social awareness, self management and social skills. These are skills which influence the manner in which people handle themselves and their relationships with others. Goleman’s position was that these competencies play a bigger role than cognitive intelligence in determining success in life and in the workplace. He and others contend that emotional intelligence involves abilities that may be categorized into five domains:
- Self awareness: Observing and recognizing a feeling as it happens.
- Managing emotions: Handling feelings so that they are appropriate; realizing what is behind a feeling; finding ways to handle fears and anxieties, anger and sadness.
- Motivating oneself; Channeling emotions in the service of a goal; emotional self control; delaying gratification and stifling impulses.
- Empathy: Sensitivity to others’ feelings and concerns and taking their perspective appreciating the differences in how people feel about things.
- Handling relationships: Managing emotions in others; social competence & social skills.
In 1995, Goleman then expanded on the works of Howard Gardner, Peter Salovey and John Mayer. He further defined Emotional Intelligence as a set of competencies demonstrating the ability one has to recognize his or her behaviors, moods and impulses and to manage them best, according to the situation. Mike Poskey, in “The Importance of Emotional Intelligence in the Workplace.” continued this definition by stating that emotional intelligence is considered to involve emotional empathy; attention to, and discrimination of one’s emotions; accurate recognition of one’s own and others’ moods; mood management or control over emotions; response with appropriate emotions and behaviors in various life situations (especially to stress and difficult situations); and balancing of honest expression of emotions against courtesy, consideration, and respect.
Source: Emotional Intelligence: what is and why it matters” – Cary Cherniss, PhD, presented at the annual conference of the Society of Industrial and Organizational Psychology, April 2000.
EQ differs from what has generally been considered intelligence which is described in terms of one’s IQ.
Traditional views of intelligence focused on cognition, memory and problem solving. Even today individuals are evaluated on the basis of cognitive skills. Entrance tests for medical, law, business, undergraduate and graduate schools base admissions in large part on the scores of the SAT, GMAT, LSAT, MCAT, etc. Without question, cognitive ability is critical but has been demonstrated, it is not a very good predictor of future direct job performance and indirect liability management. In fact, in 1940, David Wechsler the developer of a widely used intelligence test made reference to “non-intellective” elements. By this Wechsler meant affective, personal and social factors.
Source: Non-Intellective factors in intelligence. Psychological Bulletin, 37, 444-445.
Goleman became aware of the work of Salovey and Mayer having trained under David McClelland and was influenced by McClelland’s concern with how little traditional tests of cognitive intelligence predicted success in life. In fact, a study of 80 PhDs in science underwent a battery of personality tests, IQ tests and interviews in the 1950s while they were graduate students at Berkeley. Forty years later they were re-evaluated and it turned out that social and emotional abilities were four times more important than IQ in determining professional success and prestige.
Source: Feist & Barron: Emotional Intelligence and academic intelligence in career and life success. Paper presented at the Annual Convention of the American Psychological Society, San Francisco, 1996.
Undoubtedly, we want to have individuals work with us who have persistence which enables to them have the energy, drive, and thick skin to develop and close new business, or to work with the patients and other members of the staff. It is important to note that working alongside one with a “good” personality may be fun, energetic, and outgoing.
However, a “good personality does not necessarily equate to success. An individual with a high EQ can manage his or her own impulses, communicate effectively, manage change well, solve problems, and use humor to build rapport in tense situations. This clarity in thinking and composure in stressful and chaotic situations is what separates top performers from weak performers.
INVESTOR’S EQ: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2025/04/06/emotional-intelligence-how-eq-can-make-you-a-better-investor/
Poskey outlined a set of five emotional intelligence competencies that have proven to contribute more to workplace achievement than technical skills, cognitive ability, and standard personality traits combined.
***
***
A. Social Competencies: Competencies that Determine How We Handle Relationships
Intuition and Empathy – Our awareness of others’ feelings, needs, and concern. He suggested that this competency is important in the workplace for the following reasons:
- Understanding others: an intuitive sense of others’ feelings and perspectives, and showing an active interest in their concerns and interests
- Patient service orientation: the ability to anticipate, recognize and meet customer’s’ (patients) needs
- People development: ability to sense what others need in order to grow, develop, and master their strengths
- Leveraging diversity: cultivating opportunities through diverse people.
B. Political Acumen and Social Skills: Our adeptness at inducing desirable responses in others. This competency is important for the following reasons:
- Influencing: using effective tactics and techniques for persuasion and desired results.
- Communication: sending clear and convincing messages that are understood by others
- Leadership: inspiring and guiding groups of people
- Change catalyst: initiating and/or managing change in the workplace
- Conflict resolution: negotiating and resolving disagreements with people
- Collaboration and cooperation: working with coworkers and business partners toward shared goals
- Team capabilities: creating group synergy in pursuing collective goals.
C. Personal Competencies: Competencies that determine how we manage ourselves
D. Self Awareness: Knowing out internal states, preferences, resources, and intuitions. This competency is important for the following reasons.
- Emotional awareness: recognizing one’s emotions and their effects and impact on those around us
- Accurate self-assessment: knowing one’s strengths and limits
- Self-confidence: certainty about one’s self worth and capabilities
- Self-Regulation: managing one’s internal states, impulses, and resources. This competency is important in the workplace for the following reasons.
- Self-control: managing disruptive emotions and impulses
- Trustworthiness: maintaining standards of honesty and integrity
- Conscientiousness: taking responsibility and being accountable for personal performance
- Adaptability: flexibility in handling change
- Innovation: being comfortable with an openness to novel ideas, approaches, and new information.
E. Self-Expectations and Motivation: Emotional tendencies that guide or facilitate reaching goals. This competency is important in the workplace for the following reasons.
- Achievement drive: striving to improve or meet a standard of excellence we impose on ourselves
- Commitment: aligning with the goals of the group or the organization
- Initiative: readiness to act on opportunities without having to be told
- Optimism: Persistence in pursuing goals despite obstacles and setbacks
A note of caution is necessary. Goleman and Salovey both stated that emotional intelligence on its own is not a strong predictor of job performance. Instead they contend that it provides the bedrock for competencies that are predictors.
Obviously, EQ is an important attribute and it behooves each of us to promote emotional intelligence in the workplace. A number of guidelines have been developed for the Consortium for Research on Emotional Intelligence in Organizations by Goleman and Cherniss. The guidelines cover 21 phases which include preparation, training, transfer and evaluation.
- Assess the organization’s needs: Determine the competencies that are most critical for effective job performance in a particular type of job. In doing so, us a valid method, such as the comparison of the behavioral interviews of superior performs and average performers. Also make sure the competencies to be developed are congruent with the organization’s culture and overall strategy.
- Assess the individual: This assessment should be based on the key competencies needed for a particular job, and the data should come from multiple sources using multiple methods to maximize credibility and validity.
- Deliver assessments with care: Give the individual information on his/her strengths and weaknesses. In doing so, try to be accurate and clear. Also, allow plenty of time for the person to digest and integrate the information. Provide feedback in a safe and supportive environment in order to minimize resistance and defensiveness. Avoid making excuses or downplaying the seriousness of deficiencies.
- Maximize choice: People are motivated to change when they freely choose to do so. As much as possible, allow people to decide whether or not they will participate in the development process, and have them change goals themselves.
- Encourage people to participate: People will be more likely to participate in development efforts if they perceive them to be worthwhile and effective. Organizational policies and procedures should encourage people to participate in development activity, and supervisors should provide encouragement and the necessary support. Motivation will be enhanced if people trust the credibility of those who encourage them to undertake the training.
- Link learning goals to personal values: People are most motivated to pursue change that fits with their values and hopes. If a change matters little to people, they won’t pursue it. Help people understand whether a given change fits with what matters most to them.
- Adjust expectations: Builds positive expectations by showing learners that social and emotional competence can be improved and that such improvement will lead to valued outcomes. Also, make sure that the learner has a realistic expectation of what the training process will involve.
- Gauge readiness: Assess whether the individual is ready for training. If the person is not ready because of insufficient motivation or other reasons, make readiness the focus of intervention efforts.
- Foster a positive relationship between the trainers and learners: Trainers who are warm, genuine, and empathic our best able to engage the learners in the change process. Select trainers who have these qualities, and make sure that they use them when working with the learners.
- Make change self-directed: Learning is more effective when people direct their own learning program, tailoring it to their unique needs and circumstances. In addition to allowing people to set their own learning goals, let them continue to be in charge of their learning throughout the program, and tailor the training approach to the individual’s learning style.
- Set clear goals: People need to be clear about what the competence is, how to acquire it, and how to show it on the job. Spell out the specific behaviors and skills that make up the target competence. Make sure that the goals are clear, specific, and optimally challenging.
- Break goals into manageable steps: change. That is more likely to occur if the change process is divided into manageable steps. Encourage both trainers and trainees to avoid being overly ambitious.
- Provide opportunities to practice: Lasting change requires sustained practice on the job and elsewhere in life. An automatic habit is being unlearned and different responses are replacing it. Use naturally occurring opportunities for practice at work, and in life. Encourage the trainees to try the new behaviors repeatedly and consistently over a period of months.
- Give performance feedback: Ongoing feedback encourages people and direct change. Provide focused and sustained feedback as the learners practice new behaviors. Make sure that supervisors, peers, friends, family members-or some combination of these- give periodic feedback on progress.
- Rely on experiential methods: Active, concrete, experiential methods tend to work best for learning social and emotional competencies. Development activities that engage all the senses and our dramatic and powerful can be especially effective.
- Build in support: Change is facilitated through ongoing support of others who are going through similar changes. Programs should encourage the formation of groups where people give each other support, throughout the change effort. Coaches and mentors also can be valuable in helping support the desired change.
- Use models: Use modern webinars, patient portals, live or videotaped models that clearly show how the competency can be used in realistic situations. Encourage learners to study, analyze, and emulate the models.
- Enhance insight: Self-Awareness is the cornerstone of emotional and social competence. Help learners acquire greater understanding about how their thoughts, feelings, and behavior affect themselves and others.
- Prevent relapse: Use relapse prevention, which helps people use lapses and mistakes as lessons to prepare themselves for further efforts.
Moreover:
- Encourage use of skills on the job: Supervisors, peers and subordinates should reinforce and reward learners for using their new skills on the job. Coaches and mentors also can serve this function. Also, provide prompts and cues, such as through periodic follow-ups. Change also is more likely to indoor. When high status persons, such as supervisors and upper-level management model it.
- Develop an organizational culture that supports learning: Change will be more enduring if the organization’s culture and tone support the change and offer a safe atmosphere for experimentation.
Finally, see if the development effort has lasting effects evaluated. When possible, find a true set of measures of the competence or skill, as shown on the job, before and after training, and also at least two months later. One-year follow-ups also are highly desirable. In addition to charting progress on the acquisition of competencies, also assess the impact on important job related outcomes, such as performance measures, and indicators of adjustments such as absenteeism, grievances, health status, etc.
Managers V. Leaders
These abilities are important for one to be successful as a manager and even more so as a leader, or physician executive. But, before we begin an examination of strategic leadership, it is necessary to make a deeper distinction between a manager and a leader. There are many different definitions as well as descriptions regarding leadership and management.
BRAND MANAGEMENT: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2025/07/07/brand-management-7-approaches-for-doctors-and-financial-advisors/
Many people talk as though leadership and management is the same thing. Fundamentally, they are quite different. Management focuses on work. We manage work activities such as money, time, paperwork, materials, equipment, and personnel, among other things. As can be found in any basic book on management, management focuses on planning, organizing, controlling, coordinating, budgeting, finance and money management as well as decision making. In effect, managers are generally those individuals who have been given their authority by virtue of their role. It is the function of a manager to ensure that the work gets done as well as to oversee the activities of others. In many healthcare organizations we find that those individuals elevated to a managerial position occur as a result of being a high performer on their previous assignment. A manager receives authority on the basis of role; while a leader’ authority is more innate in nature.
HEALTHCARE LEADERSHIP: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2025/05/01/healthcare-leadership-on-the-brink-executives-eyeing-the-exits/
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
***
***
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
Like, Subscribe and Refer
***
Filed under: Ask a Doctor, Career Development, Ethics, Glossary Terms, LifeStyle, Management, Marcinko Associates, mental health, Risk Management, Touring with Marcinko | Tagged: A.I., Cary Cherniss, Daniel Goleman, david marcinko, Emotional Intelligence, empathy, EQ, Gary A. Cook, gene schmuckler, Howard Gardner, intelligence quota, IQ, John Mayer, leadership, Management, personal-development, self-awareness | Leave a comment »