
US Healthcare Expenditures Reaching Unsustainable Levels
[By Sam Muppalla]
Vice President: McKesson Health Solutions, Network Performance Management (NPM)
Expenditures on healthcare in the United States continue to increase and are rapidly reaching unsustainable levels. Pressures by businesses, households and the government to address these escalating costs and ensure high-quality healthcare are multiplying.
This is the first in a series of six essays that examine the challenges facing health plans and the ways that network design can unlock affordable care by aligning products, care models, and reimbursement.
Health insurance companies are faced with addressing a rapidly changing healthcare environment on multiple fronts. These changes are being driven by the goal of achieving a more affordable, higher quality healthcare system. Shifting market needs, increased regulatory initiatives, and a demand for administrative efficiency are requiring innovative approaches to unlocking affordable care. These pressures are originating from key healthcare stakeholders—employers, members and the government (Figure 1).
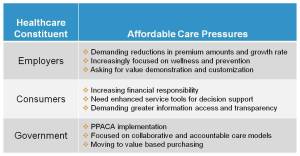
Employer Pressure
As the competition for the group insurance market increases, health plans need to respond to employer demands for products that deliver greater value. Delivering high value requires products which are tailored to the health of the employer’s specific population and emphasize wellness and prevention. An employer that can offer benefits and programs tailored to meet their employee needs can both improve their workforce productivity and optimize their healthcare spend. The employer’s insistence for reduction in premiums and decrease in the rate of premium growth is challenging health plans to develop more innovative strategies.
Consumer/Member Pressure
With the passage of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act of 2010 (PPACA), the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates (Figure 2) that approximately 32 million more individuals will require access to healthcare services. This represents a significant increase in the number of new healthcare consumers at a time when health insurance companies are required to guarantee issue and re-newability of coverage. Steering this influx of new members to the right care teams will be a very critical core competency for health plans to develop. It is one of the few risk management tools left in the plan’s arsenal in a guaranteed access world. The growth of the individual market is also being accompanied by an increase in member financial responsibility. Members are increasingly demanding greater transparency into their provider quality, performance and cost information.
Government/Regulatory Pressure
Evolving healthcare regulation puts still more pressure on health plans. New regulations within the PPACA Section 9016, stipulate an 80% MLR cap for small groups (fewer than 100 lives) and an 85% Medical Loss Ratio (MLR) cap for large groups (more than 100 lives). These regulations also cap the percentage of revenues that can be earmarked for operational and administrative expenses at 15-20%. This poses a unique challenge for health plans; it requires plans to innovate in the areas of products, care models, and reimbursement designs without increasing the administrative and operational overhead.
There are roughly eighteen additional PPACA provisions that put further pressure on health plans by promoting increased collaboration (sections: 6301, 4201, 3027, 3011, 3021, 10333, 3022, 3024) and accountability (sections: 2705, 3006 & 10301, 3001, 3025, 2706, 2704, 3023, 3004, 3008 and 3002). The Bureau of National Affairs best summarized these provisions by stating,
“The comprehensive provisions in the act regarding payment and delivery reform reflect both the payment system continuum—from fee-for-service to bonus incentives for quality to bundled payments to partial and full global payments as well as the delivery system continuum—from independent clinicians and hospitals to small group practices to multi-provider networks to partially or virtually integrated organizations to fully integrated systems with common ownership and employment.”
These demands mean that health plans need to offer new high-value products that incorporate outcome-based reimbursement to drive quality outcomes and not pay for potentially avoidable costs.
According to studies by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation and Prometheus Payment (2009), “Up to 40 cents of every dollar spent on chronic conditions and 15 to 20 cents of every dollar spent on acute hospitalization and procedures are attributable to potentially avoidable complications (PACs).”
With evidence like this health plans are taking a new, hard look at when and how care is delivered.
Assessment
Next time, we’ll be looking at how health plans are responding to these challenges with innovations in products, care models, and reimbursement structures. Visit the blog next week for “The Three Levers of Innovation for Care Affordability.”
If you can’t wait, you can read the entire Unlocking Affordable Care by Aligning Products white paper now; it’s available on our website.
A Webinar
On December 8th, we’ll be hosting a webinar on Lean Provider Lessons for Post Reform Success. Plan to attend this free webinar for more insights into designing for affordable high-quality care.
Channel Surfing the ME-P
Have you visited our other topic channels? Established to facilitate idea exchange and link our community together, the value of these topics is dependent upon your input. Please take a minute to visit. And, to prevent that annoying spam, we ask that you register. It is fast, free and secure.
Conclusion
Your thoughts and comments on this ME-P are appreciated. Feel free to review our top-left column, and top-right sidebar materials, links, URLs and related websites, too. Then, subscribe to the ME-P. It is fast, free and secure.
Speaker: If you need a moderator or speaker for an upcoming event, Dr. David E. Marcinko; MBA – Publisher-in-Chief of the Medical Executive-Post – is available for seminar or speaking engagements. Contact: MarcinkoAdvisors@msn.com
OUR OTHER PRINT BOOKS AND RELATED INFORMATION SOURCES:






Filed under: Health Economics, Health Insurance, Healthcare Finance, Op-Editorials, Quality Initiatives, Videos | Tagged: ACA, Bureau of National Affairs, Health insurance companies, McKesson Health Solutions, Medical Loss Ratio, Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, Prometheus Payment, Sam Muppalla, US Healthcare Expenditures | 7 Comments »

























