By Dr. David Edward Marcinko; MBA MEd
SPONSOR: http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
***
***
Philanthropy is often celebrated as a noble endeavor, allowing wealthy individuals to contribute to societal welfare. However, beneath its altruistic veneer, philanthropic giving can also function as a strategic financial tool—particularly as a form of tax shelter. This duality raises important questions about equity, influence, and the role of private wealth in shaping public outcomes.
At its core, a tax shelter is any legal strategy that reduces taxable income. In the case of philanthropy, the U.S. tax code allows individuals to deduct charitable donations from their taxable income, often up to 60% depending on the type of donation and recipient organization. For billionaires and high-net-worth individuals, this can translate into substantial tax savings. For example, donating appreciated stock or real estate not only earns a deduction for the full market value but also avoids capital gains taxes that would have been incurred through a sale.
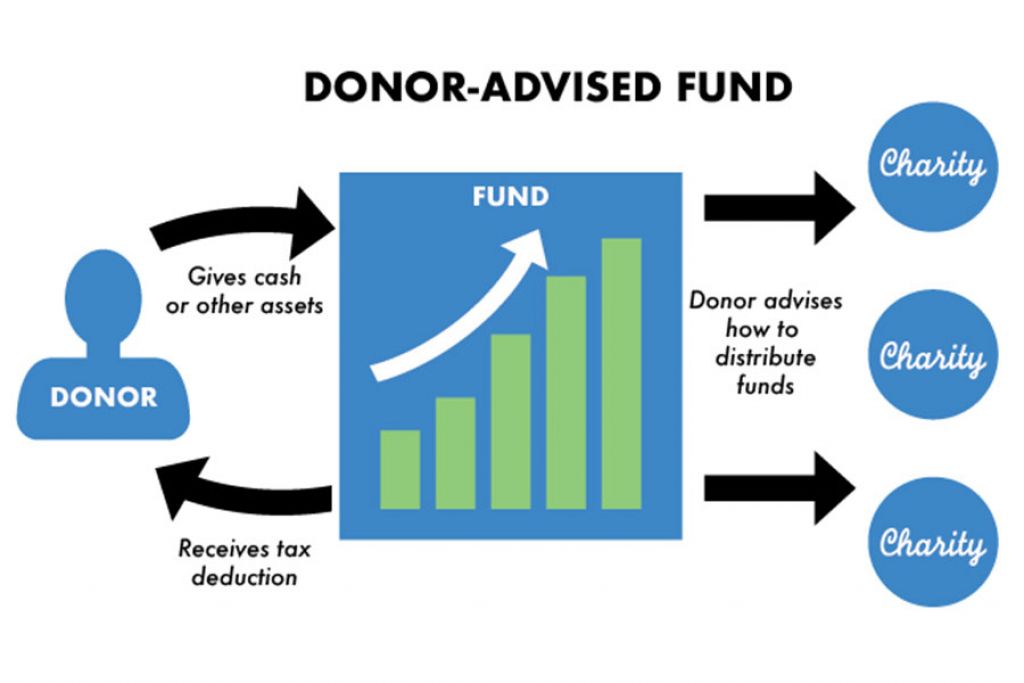
One common vehicle for such giving is the donor-advised fund (DAF). These funds allow donors to make a charitable contribution, receive an immediate tax deduction, and then distribute the money to charities over time. While DAFs offer flexibility and convenience, critics argue they enable donors to delay actual charitable impact while still reaping tax benefits. In some cases, funds sit idle for years, raising concerns about whether the public good is truly being served.
Private foundations present another avenue for tax-advantaged giving. By establishing a foundation, donors can retain significant control over how their money is spent, often employing family members or influencing policy through grantmaking. While foundations are required to distribute a minimum of 5% of their assets annually, this threshold is relatively low, and administrative expenses can count toward it. This means that a large portion of foundation assets may remain invested, growing tax-free, while only a fraction is used for charitable work.
Beyond financial mechanics, philanthropic tax shelters raise ethical and democratic concerns. When wealthy individuals use charitable giving to reduce their tax burden, they effectively shift resources away from public coffers—funds that could support schools, infrastructure, or healthcare. Moreover, philanthropy allows donors to direct resources according to personal priorities, which may not align with broader societal needs. This privatization of public influence can undermine democratic decision-making and perpetuate inequality.
In conclusion, while philanthropic giving can yield positive social outcomes, it also serves as a powerful tax shelter for the wealthy. The challenge lies in balancing the benefits of private generosity with the need for transparency, accountability, and equitable tax policy. As debates over wealth concentration and tax reform intensify, reexamining the role of philanthropy in public finance becomes increasingly urgent. Only by addressing these complexities can society ensure that charitable giving truly serves the common good.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com -OR- http://www.MarcinkoAssociates.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", Ethics, Funding Basics, Glossary Terms, iMBA, Inc., Portfolio Management, Touring with Marcinko | Tagged: Accounting, charity, DAFs, david marcinko, donar advised funds, Ethics, finance, Giving, grants, Investing, money, personal-finance, philanthropy, tax, tax shelters | Leave a comment »