FINANCIAL DEFINITIONS
By Dr. David Edward Marcinko MBA MEd
***
***
Macaulay duration is a foundational concept in fixed-income investing that measures the weighted average time until a bondholder receives the bond’s cash flows. It is essential for understanding interest rate risk and managing bond portfolios.
Named after economist Frederick Macaulay, Macaulay duration represents the average time in years that an investor must hold a bond to recover its present value through coupon and principal payments. Unlike simple maturity, which only reflects the final payment date, Macaulay duration accounts for the timing and magnitude of all cash flows, weighted by their present value. This makes it a more precise tool for evaluating a bond’s sensitivity to interest rate changes.
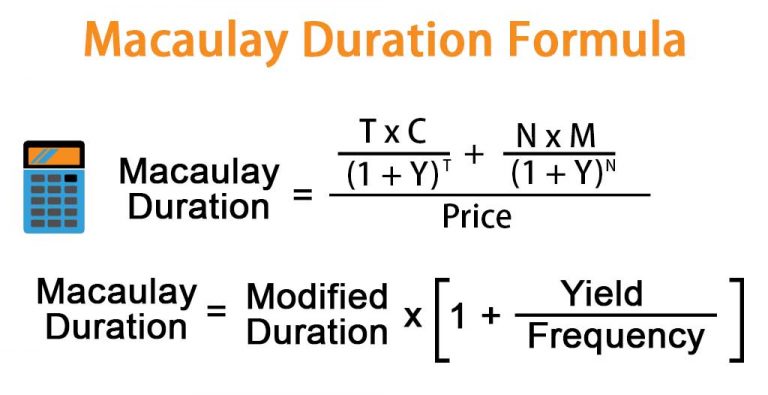
To calculate Macaulay duration, each cash flow is discounted to its present value using the bond’s yield to maturity. These present values are then weighted by the time at which each payment occurs. The formula is:
Macaulay Duration=∑t=1n(t⋅CFt(1+y)t)P\text{Macaulay Duration} = \frac{\sum_{t=1}^{n} \left( \frac{t \cdot CF_t}{(1+y)^t} \right)}{P}
Where CFtCF_t is the cash flow at time tt, yy is the yield to maturity, and PP is the bond’s price. The result is expressed in years.
Why does this matter? Macaulay duration is crucial for investors who want to match the timing of their liabilities with their assets—a strategy known as immunization. By aligning the duration of a bond portfolio with the time horizon of future liabilities, investors can minimize the impact of interest rate fluctuations. For example, pension funds often use duration matching to ensure they can meet future payouts regardless of rate changes.
Duration also helps investors compare bonds with different maturities and coupon structures. Generally, bonds with longer maturities and lower coupons have higher durations, meaning they are more sensitive to interest rate changes. Conversely, short-term or high-coupon bonds have lower durations and are less affected by rate shifts.
While Macaulay duration is a powerful tool, it has limitations. It assumes a flat yield curve and constant interest rates, which rarely hold true in dynamic markets. For more precise risk management, investors often use modified duration, which adjusts Macaulay duration to estimate the percentage change in a bond’s price for a 1% change in interest rates.
In practice, Macaulay duration is most useful for long-term planning and strategic asset allocation. It provides a clear measure of time-weighted cash flow exposure and helps investors build portfolios that are resilient to interest rate volatility.
Whether used for individual bond selection or broader portfolio construction, understanding Macaulay duration equips investors with a deeper grasp of fixed-income dynamics.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
SPEAKING: Dr. Marcinko will be speaking and lecturing, signing and opining, teaching and preaching, storming and performing at many locations throughout the USA this year! His tour of witty and serious pontifications may be scheduled on a planned or ad-hoc basis; for public or private meetings and gatherings; formally, informally, or over lunch or dinner. All medical societies, financial advisory firms or Broker-Dealers are encouraged to submit an RFP for speaking engagements: CONTACT: Ann Miller RN MHA at MarcinkoAdvisors@outlook.com
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", finance, Portfolio Management | Tagged: bond duration, bonds, coupons, duration, finance, Frederick Macaulay, immunization, interest rates, Investing, IRS, Macaulay fixed income duration, personal-finance, principles, stocks | Leave a comment »