A Supply Chain Management Strategy
By Staff Reporters
***
***
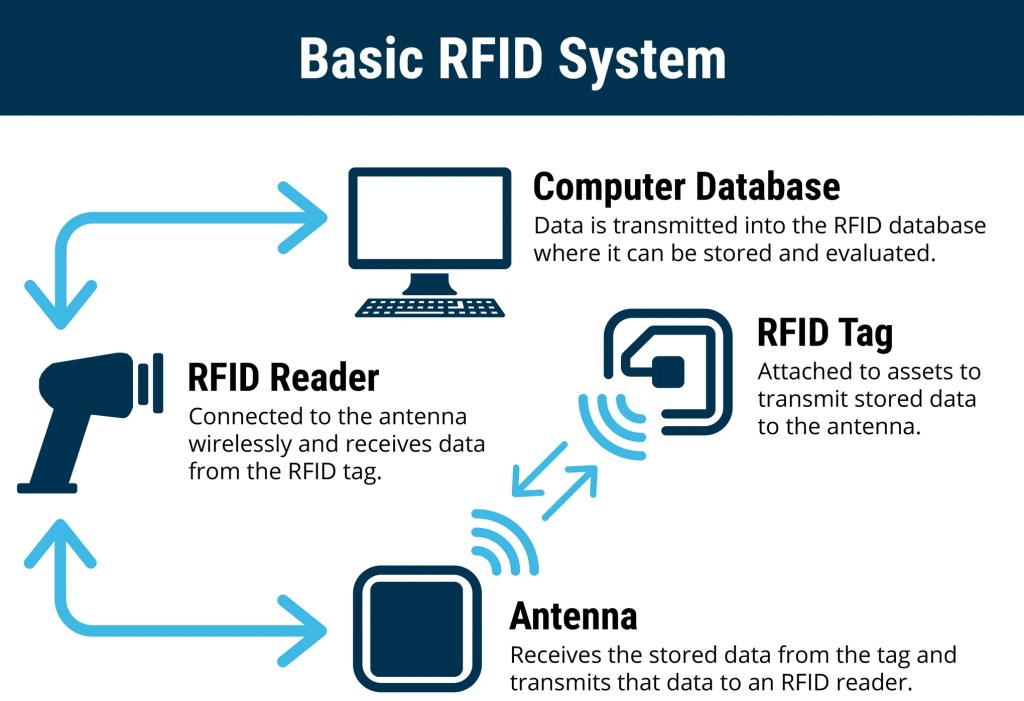
RADIO FREQUENCY IDENTIFICATION
RFID refers to a device attached to an object that transmits data to an RFID receiver. A device can be a large piece of hospital hardware the size of a small book like those attached to ocean containers, or a very small device inserted into a label on a package. RFID has advantages over bar codes such as the ability to hold more data, and to change the stored data as processing occurs. Moreover, it does not require line-of-sight to transfer data, and is very effective in harsh environments where bar-code labels will not work. RFID is not without its own problems, however, as RF signals can be compromised by materials such as metals and liquids.
SCM: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2011/06/09/supply-chain-management-in-healthcare/
Although RFID technology is receiving much current attention, it still tends to be cost-prohibitive for some hospital inventory tracking applications. As chip prices go down, there will be continued growth in the application of RFID, but, as in the case of 2D bar codes, many hospital warehouse applications simply do not require this added functionality. The low-cost 1D bar code may continue to be the technology of choice for many hospital inventory tracking applications in the short term.
Smart labels are labels with integrated RFID chips. The idea is to produce labels (probably with bar codes) as well as programming the RFID chips embedded in the label. This would provide all current functionality (human- and machine-readable text and bar codes) as well as adding RFID functionality.
Slap-and-ship describes an approach to complying with vendor requirements for physical identification of shipped goods. More recently, slap-and-ship has been used to describe complying With RFID requirements (such as those from large health care systems); however, it is also applicable to any compliance labeling requirement (such as compliance bar-code labels). Slap-and-ship implies meeting the customer’s requirement by applying the bar-code labels or RFID tags, but not utilizing the technology internally.
SCM PODCAST: https://medicalexecutivepost.com/2022/03/16/podcast-medical-supply-chain-management/
Finally, anti-skimming bills were first approved by California and Washington State relative to RFID privacy and are focused on making it illegal for criminals or businesses (or criminal businesses) to read and use personal information from RFID-enabled items such as driver’s licenses and credit cards without the owner’s consent.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
Like and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: "Ask-an-Advisor", business, Glossary Terms, Health Economics, Information Technology, Videos | Tagged: artificial intelligence, logistics, marketing, Radio Frequency Identification, RFID, SCM, skimming, slap andship, smart abel, supply chain management, Technology | Leave a comment »