By Staff Reporters
***
***
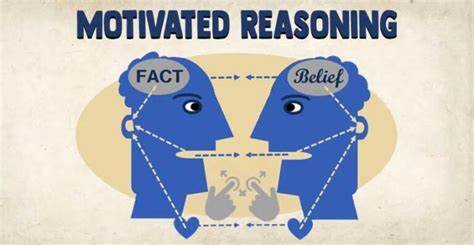
Motivated Reasoning is the tendency to process information in a way that aligns with your desires and preconceptions. It’s like having rose-colored glasses for your beliefs.
Motivated reasoning (motivational reasoning bias) is a cognitive and social response in which we, consciously or sub-consciously, allow emotion-loaded motivational biases to affect how new information is perceived. Individuals tend to favor evidence that coincides with their current beliefs and reject new information that contradicts them, despite contrary evidence.
According to Wikipedia, motivated reasoning can be classified into two categories: 1) Accuracy-oriented (non-directional), in which the motive is to arrive at an accurate conclusion, irrespective of the individual’s beliefs, and 2) Goal-oriented (directional), in which the motive is to arrive at a particular conclusion.
Furthermore, colleague Dan Ariely PhD suggests that when we encounter any new information, we twist and turn it to fit our existing views. This mental gymnastics helps us avoid cognitive dissonance but can also lead us astray.
So, next time you’re defending your viewpoint, ask yourself: am I seeing this clearly, or is it motivated reasoning at play?
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
Subscribe Today!
***
***
Filed under: "Doctors Only", Career Development, Ethics, Experts Invited, LifeStyle, mental health | Tagged: accuracy orientation, beliefs, bias, cogmitive dissonance, cognitive, Dan Ariely, facts, glasses, goal orientation, mental health, motivated reasoning, motivation, reasoning, riose colored reasoning, rose color glasses, wilipedia | Leave a comment »