By Artificial Intelligence
***
***
Quantum mechanics is a fundamental branch of physics that explores the behavior of matter and energy at the smallest scales—typically atomic and subatomic levels. Unlike classical physics, which deals with predictable and continuous phenomena, quantum mechanics reveals a world governed by probabilities, uncertainties, and strange dualities. It challenges our intuitive understanding of reality and has revolutionized both science and technology.
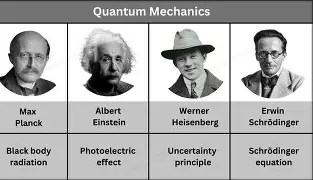
The origins of quantum mechanics trace back to the early 20th century, when classical theories failed to explain certain experimental results. Max Planck’s work on black-body radiation in 1900 introduced the idea that energy is quantized, meaning it comes in discrete packets called “quanta.” This concept laid the foundation for quantum theory. Soon after, Albert Einstein explained the photoelectric effect by proposing that light itself is made of particles—later called photons—further reinforcing the idea of quantization.
One of the most striking features of quantum mechanics is wave-particle duality. According to this principle, particles such as electrons and photons exhibit both wave-like and particle-like behavior depending on how they are observed. This duality was famously demonstrated in the double-slit experiment, where particles create an interference pattern typical of waves when not observed, but behave like particles when measured.
Another cornerstone of quantum mechanics is Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle, which states that certain pairs of physical properties—like position and momentum—cannot both be known precisely at the same time. This introduces a fundamental limit to measurement and implies that the act of observing a system can alter its state.
Quantum mechanics also introduces the concept of superposition, where particles can exist in multiple states simultaneously until measured. This idea is illustrated by Schrödinger’s cat thought experiment, in which a cat in a sealed box is both alive and dead until the box is opened and the cat is observed. Though metaphorical, this paradox highlights the non-intuitive nature of quantum systems.
Perhaps the most mysterious phenomenon in quantum mechanics is entanglement. When particles become entangled, their states are linked regardless of the distance between them. A change in one particle instantly affects the other, defying classical notions of locality. This “spooky action at a distance,” as Einstein called it, has been experimentally confirmed and is the basis for emerging technologies like quantum cryptography and quantum teleportation.
Quantum mechanics is not just theoretical—it has practical applications that shape our modern world. Technologies such as lasers, semiconductors, MRI machines, and atomic clocks all rely on quantum principles. Moreover, quantum computing promises to revolutionize information processing by using quantum bits (qubits) that can represent multiple states simultaneously, enabling calculations far beyond the reach of classical computers.
In conclusion, quantum mechanics is a profound and essential framework for understanding the universe at its most fundamental level. It challenges our perceptions, fuels technological innovation, and continues to inspire scientists and philosophers alike. As research advances, quantum mechanics may unlock even deeper mysteries of reality, reshaping our understanding of existence itself.
COMMENTS APPRECIATED
Like, Refer and Subscribe
***
***
Filed under: Ask a Doctor, Ethics, Experts Invited | Tagged: AI, albert einstein, entanglements, Erwin Schrodinger, Max Planc, microscopic universe, philosophy, physics, quantum mechanics, quantum-physics, qubits, Science, superposition, Werner Heisenberg | Leave a comment »